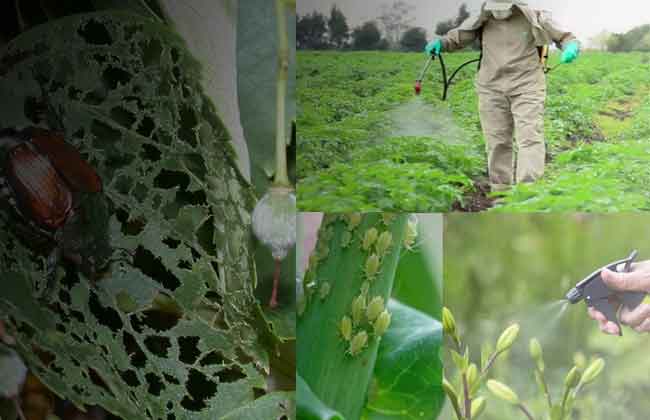
Pest and disease management: Pest and disease management are essential practices in agriculture, horticulture, and forestry. Pests and diseases can have a significant impact on crop yield, quality, and profitability. It is, therefore, necessary to adopt appropriate measures to prevent, monitor, and control pest and disease infestations. In this article, we will discuss the different types of pests and diseases and various management strategies.
Types of pests and diseases:
Pests are organisms that damage or cause harm to plants, animals, and humans. Pests can be classified into two broad categories: vertebrate and invertebrate pests. Vertebrate pests include animals like rats, mice, birds, and rabbits. Invertebrate pests include insects, mites, and nematodes.
Diseases are caused by microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, viruses, and phytoplasmas. These microorganisms infect the plants and cause a range of symptoms like leaf spots, wilting, yellowing, stunting, and death.
Management strategies:
Pest and disease management involves a range of practices that are aimed at preventing, monitoring, and controlling pest and disease infestations. Here are some of the management strategies that can be used:
- Cultural practices:
Cultural practices like crop rotation, intercropping, and mixed cropping can help to reduce pest and disease infestations. Crop rotation involves alternating crops on a piece of land to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases. Intercropping involves planting different crops together in the same field, which can confuse pests and reduce the risk of infestations. Mixed cropping involves planting different crops together, which can also help to reduce pest and disease infestations.
- Biological control:
Biological control involves the use of natural enemies like predators, parasites, and pathogens to control pest and disease infestations. This method is environmentally friendly and can be effective in controlling pests and diseases.
- Chemical control:
Chemical control involves the use of pesticides to control pest and disease infestations. This method can be effective in controlling pests and diseases, but it can also have adverse effects on the environment and human health. It is, therefore, essential to use pesticides responsibly and follow the label instructions.
- Mechanical control:
Mechanical control involves the use of physical methods like trapping, pruning, and weeding to control pest and disease infestations. This method can be effective in controlling pests and diseases, but it can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
- Integrated pest management:
Integrated pest management (IPM) is an approach that involves the use of a combination of different management strategies to control pest and disease infestations. This approach is more sustainable and can be effective in controlling pests and diseases. IPM involves monitoring the pest and disease populations, identifying the pest and disease species, and choosing the appropriate management strategy.
Steps in Pest and Disease Management:
- Monitoring:
The first step in pest and disease management is monitoring. Monitoring involves inspecting the crops regularly to identify pest and disease infestations. This step is essential in identifying the type and severity of pest and disease infestations and choosing the appropriate management strategy.
- Identification:
After monitoring, the next step is to identify the pest and disease species. This step is crucial in choosing the appropriate management strategy. Identification can be done using field guides, diagnostic tools, and laboratory analysis.
- Prevention:
Prevention is an essential step in pest and disease management. Prevention involves adopting cultural practices like crop rotation, intercropping, and mixed cropping to reduce the risk of pest and disease infestations.
Read Also: Irrigation and Water Management
![]()






2 thoughts on “Pest and Disease Management”