How to Analyze Stocks: Investing in the stock market can be both exciting and daunting. While there is no guaranteed formula for success, analyzing stocks is a crucial step towards making informed investment decisions. By employing various analytical techniques and considering key factors, investors can enhance their chances of selecting promising stocks. In this article, we will explore a step-by-step guide on how to analyze stocks, providing you with the tools to navigate the stock market with confidence.
I. Fundamental Analyze Stocks: Understanding the Company
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating the financial health and performance of a company. By examining its financial statements, industry position, and competitive advantage, investors gain insights into a stock’s value and potential for growth. Key aspects to consider include:
- Financial Statements:
- Income Statement: Analyze revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period to assess profitability.
- Balance Sheet: Evaluate assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity to gauge financial stability and leverage.
- Cash Flow Statement: Examine cash inflows and outflows to understand the company’s liquidity and ability to generate free cash flow.
- Industry Analysis:
- Study the industry in which the company operates, identifying growth prospects, market trends, and competitive dynamics.
- Evaluate the company’s position within the industry, including market share, product differentiation, and barriers to entry.
- Competitive Advantage:
- Determine the company’s unique strengths, such as patents, brand recognition, or cost leadership, which give it a competitive edge.
- Assess the sustainability of the company’s competitive advantage over the long term.
II. Technic for Analyze Stocks: Interpreting Stock Price Patterns
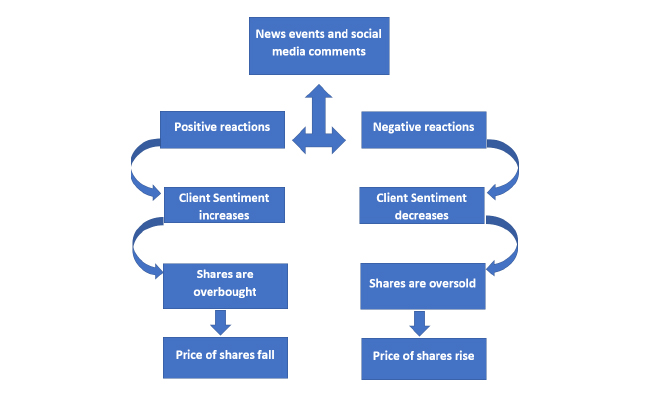
Technical analysis focuses on studying historical stock price and volume data to predict future price movements. This analysis assumes that historical patterns tend to repeat and that market trends can be identified. Key techniques include:
- Chart Patterns:
- Identify common chart patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and triangles to predict price reversals or continuations.
- Use technical indicators like moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) to confirm or signal potential trends.
- Support and Resistance Levels:
- Determine price levels where the stock has historically found support (bouncing back) or resistance (stalling) and analyze their significance.
- Monitor breakouts or breakdowns from these levels as potential buying or selling opportunities.
III. Ratio Analysis: Assessing Financial Performance
Ratio analysis involves comparing various financial ratios to evaluate a company’s performance, profitability, and efficiency. Key ratios to consider include:
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio:
- Compare a company’s stock price with its earnings per share (EPS) to determine if the stock is overvalued or undervalued.
- Compare the P/E ratio with industry peers to assess relative valuation.
- Return on Equity (ROE):
- Evaluate how effectively a company utilizes shareholder equity to generate profits.
- Higher ROE indicates better management efficiency and potential for higher returns.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
- Analyze the proportion of debt to equity to assess the company’s financial leverage and risk.
- A lower ratio indicates a lower debt burden and potentially less financial risk.
IV. Qualitative Analysis: Evaluating Non-Financial Factors
Apart from financial analysis, it’s important to consider qualitative factors that can impact a company’s performance:
- Management Team:
- Assess the quality and track record of the company’s management team.
- Look for experienced leaders with a clear vision and a history of successful execution.
- Competitive Landscape:
- Analyze the company’s position within the competitive landscape and its ability to adapt to changes.
- Consider industry trends, disruptive technologies, and regulatory factors that may impact the company’s prospects.
- Growth Opportunities:
- Identify potential catalysts for growth, such as new product launches, expansion into new markets, or strategic partnerships.
Analyzing stocks is a multifaceted process that combines fundamental, technical, ratio, and qualitative analysis. By diligently researching and considering these factors, investors can make more informed investment decisions. Remember, investing in stocks carries inherent risks, and no analysis can guarantee success. It’s crucial to diversify your portfolio, set realistic expectations, and stay updated on market trends. With practice and continuous learning, you can enhance your ability to analyze stocks and increase your chances of investment success in the dynamic world of the stock market.
Read Also: Growth Investing Strategies
![]()