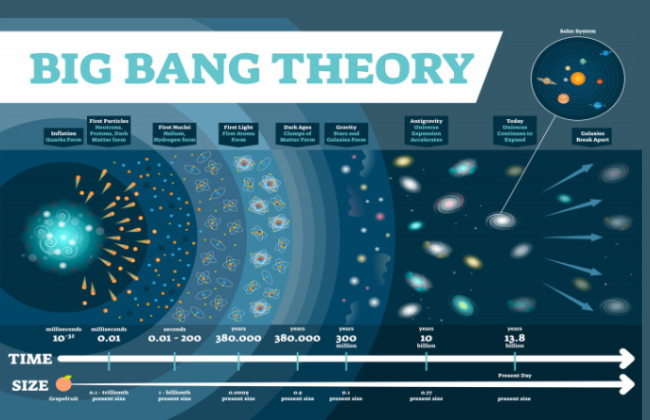
The Big Bang Theory is a widely accepted scientific explanation for the origins of the universe. The theory suggests that the universe began as a singularity, a point of infinite density and temperature, which expanded rapidly in a process known as cosmic inflation. This expansion led to the formation of the universe as we know it today, including the formation of stars, galaxies, and planets.
The theory is supported by a wide range of observations and measurements, including the cosmic microwave background radiation, the abundance of light elements in the universe, and the large-scale distribution of galaxies. However, despite its success in explaining many aspects of the universe, the Big Bang Theory is still an area of active research and debate among scientists.
One of the key pieces of evidence for the Big Bang Theory is the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). This radiation is a faint glow of microwaves that fills the universe, and it is thought to be a remnant of the hot, dense state of the universe just after the Big Bang. The CMB was first discovered in 1964 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, and its discovery was a crucial confirmation of the Big Bang Theory.
Another piece of evidence for the Big Bang Theory is the abundance of light elements in the universe, such as hydrogen and helium. These elements were formed in the early universe through a process known as nucleosynthesis, which was driven by the high temperatures and densities of the early universe. The predicted abundances of these light elements match very closely with observations, providing strong support for the Big Bang Theory.
The large-scale distribution of galaxies is also consistent with the predictions of the Big Bang Theory. The theory suggests that the universe should be homogeneous and isotropic on large scales, meaning that it should look the same in all directions. This prediction has been borne out by observations of the large-scale distribution of galaxies, which show a uniformity that is consistent with the theory.
Despite its successes, the Big Bang Theory is still an area of active research and debate. One of the key challenges for the theory is the problem of dark matter and dark energy. These mysterious substances are thought to make up the majority of the mass-energy content of the universe, yet their nature is still not well understood. Many scientists are working to develop new theories that can explain these phenomena and build on the foundation of the Big Bang Theory.
Another area of active research is the study of cosmic inflation, the period of rapid expansion that is thought to have occurred in the early universe. While the idea of cosmic inflation is widely accepted, there is still much that is not well understood about how it occurred and what caused it. Scientists are working to develop new observational and theoretical tools to study cosmic inflation and deepen our understanding of this crucial period in the history of the universe.
Overall, the Big Bang Theory is a powerful and compelling explanation for the origins of the universe. Its success in explaining a wide range of phenomena has led to a deepening of our understanding of the universe and our place within it. However, there is still much that is not well understood, and the theory is likely to continue to evolve and develop in the years to come.
![]()