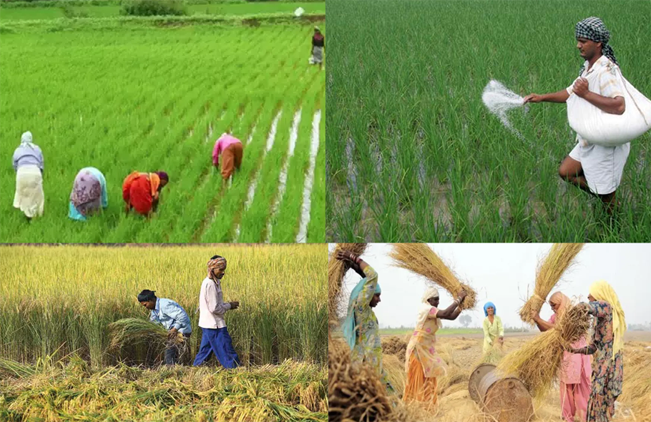
Crop Management and Production: Crop management and production are essential aspects of agriculture. Effective crop management practices are necessary for maximizing yields, minimizing losses, and ensuring sustainable production. In this article, we will explore the key elements of crop management and production.
Crop Selection
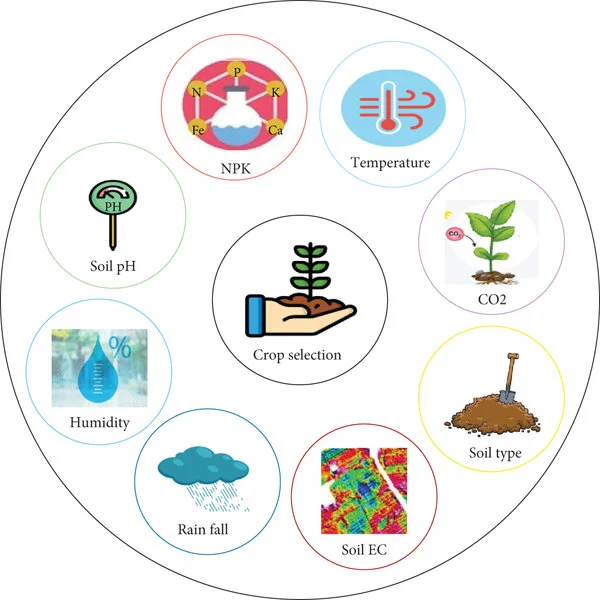
Crop selection is the first step in crop management and production. The choice of crop to plant depends on various factors, including climate, soil type, and market demand. It is essential to select crops that are suitable for the specific growing conditions and can provide maximum yields.
Soil Preparation
Before planting, the soil must be properly prepared. Soil preparation involves removing weeds, rocks, and other debris that could hinder plant growth. It also includes tilling the soil to loosen it and create a suitable seedbed for planting. The use of fertilizers and soil amendments may also be necessary to improve soil fertility and enhance plant growth.
Planting
Planting is a critical aspect of crop management and production. The timing and method of planting can significantly impact crop yields. The ideal planting time varies depending on the crop and growing conditions. For example, some crops may be planted in the spring, while others are better suited for fall planting. The planting method, such as direct seeding or transplanting, may also affect crop yields.
Irrigation
Water is essential for plant growth, and irrigation is necessary in areas where rainfall is insufficient. Effective irrigation management is critical for maximizing yields and reducing water usage. Different crops have different water requirements, and the irrigation system must be tailored to meet those needs. Over-irrigation can lead to waterlogging and soil erosion, while under-irrigation can cause plant stress and reduced yields.
Fertilization
Fertilization is an essential aspect of crop management and production. Fertilizers provide plants with essential nutrients that are necessary for growth and development. Different crops have different nutrient requirements, and the type and amount of fertilizer applied must be adjusted accordingly. Over-fertilization can lead to nutrient runoff and environmental pollution, while under-fertilization can result in reduced yields.
Pest Management
Pest management is necessary to protect crops from pests, diseases, and other harmful organisms. Various pest control methods are available, including chemical and biological methods. Integrated pest management (IPM) is a holistic approach that combines different pest control methods to achieve maximum results with minimal environmental impact.
Weed Control
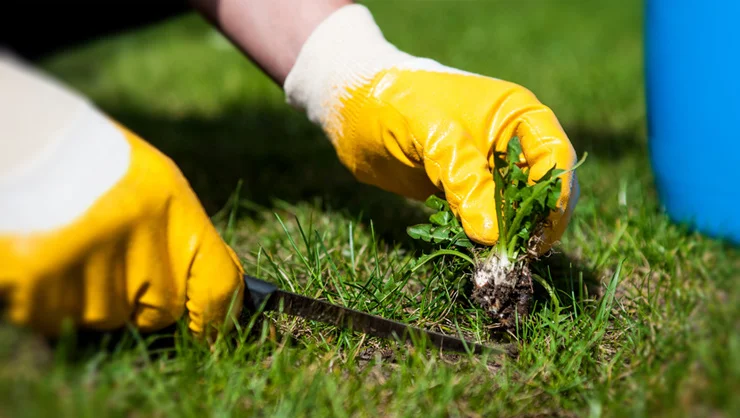

Weeds compete with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight, and can significantly reduce yields. Effective weed control is necessary to minimize weed pressure and maximize crop yields. Different weed control methods are available, including mechanical, chemical, and cultural methods. Crop rotation and cover cropping can also be effective in controlling weeds.
Harvesting
Harvesting is the process of gathering crops at the end of the growing season. The timing of harvesting is critical, as it can significantly impact crop quality and yield. Different crops have different harvest times, and the method of harvesting may vary depending on the crop and growing conditions.
Storage and Transportation
After harvesting, crops must be properly stored and transported to maintain quality and prevent losses. The storage conditions, such as temperature and humidity, must be carefully controlled to prevent spoilage and deterioration. Transportation must also be carefully managed to prevent damage to crops during transit.
Sustainability
Sustainable crop management and production practices are necessary to ensure long-term agricultural productivity and environmental health. Sustainable practices aim to maximize yields while minimizing environmental impact. This involves using resources efficiently, minimizing waste, and preserving natural resources such as soil, water, and biodiversity.
Effective crop management and production practices are critical for maximizing yields, minimizing losses, and ensuring sustainable agriculture. Crop selection, soil preparation, planting, irrigation, fertilization, pest management, weed control, harvesting, and storage are all essential components of crop management.
Read Also: Organic Farming and Food Production
![]()





