Introduction:
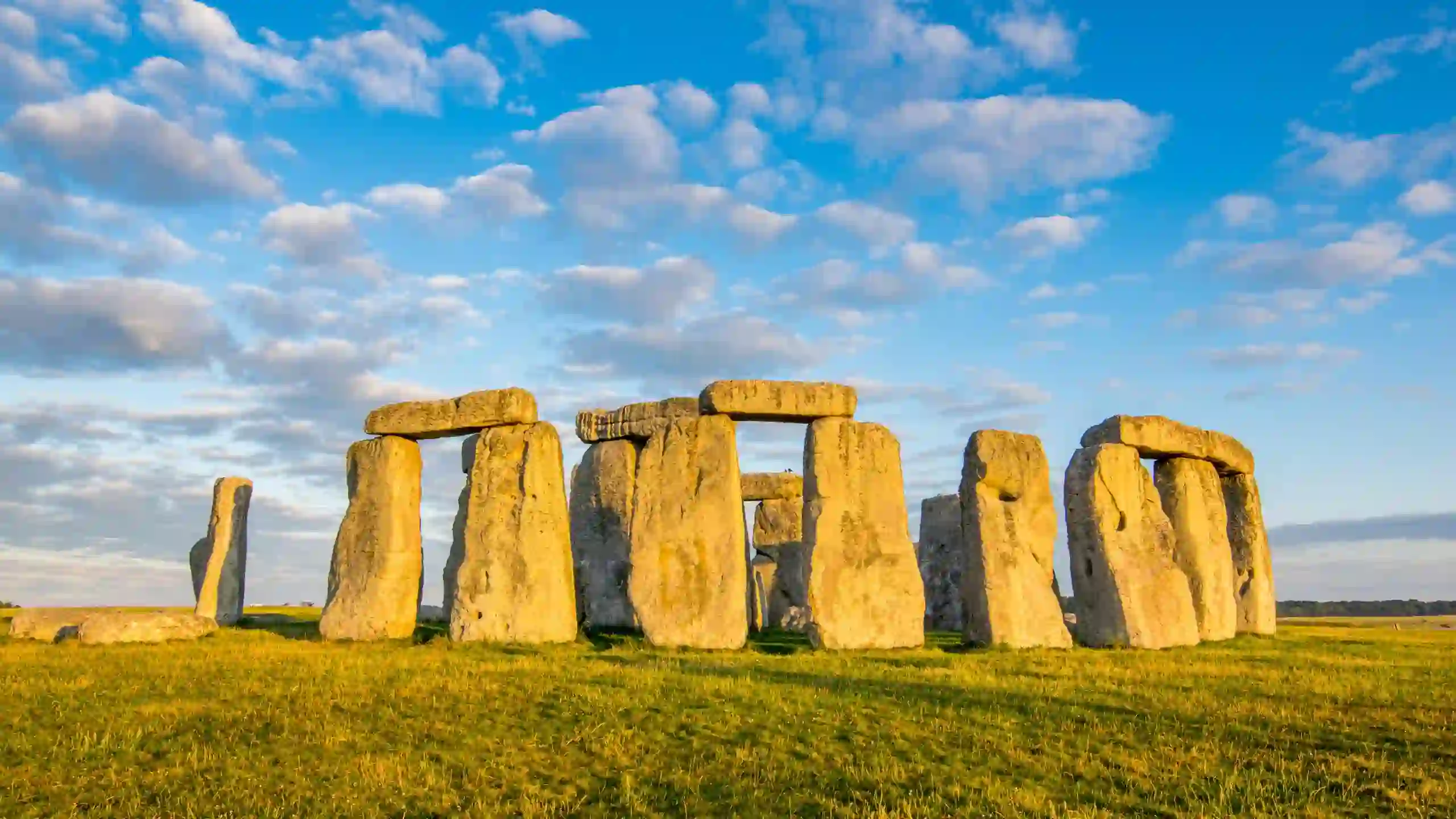
Stonehenge, a prehistoric monument located in Wiltshire, England, stands as one of the most enigmatic and awe-inspiring ancient wonders. Its massive stone circle, constructed over 4000 years ago, continues to captivate the imagination of people worldwide. With its mysterious origins and purpose, Stonehenge remains an enduring symbol of human ingenuity and the power of ancient civilizations. In this article, we delve into the fascinating history, theories, and significance of this extraordinary archaeological site.
- Origins and Construction:
The origins of Stonehenge date back to the Neolithic period, around 2500 BCE. It is believed that the monument was built in several phases over a span of 1,500 years. The first phase involved the construction of a circular ditch and a bank. The iconic standing stones, known as sarsens, were erected later, creating the outer circle. The inner horseshoe-shaped structure consists of smaller bluestones, some weighing up to four tons, believed to have been transported from the Preseli Hills in Wales, over 150 miles away.
- Theories and Purpose:
The purpose of Stonehenge has puzzled archaeologists, historians, and scientists for centuries. Several theories have emerged to explain its significance. One prevailing theory suggests that it served as an ancient astronomical observatory, aligned with the movements of the sun and moon. Another theory proposes that Stonehenge was a ceremonial site, where ancient rituals and religious ceremonies took place. Yet, there are other theories suggesting it was a burial ground or a healing center. The true purpose of Stonehenge remains an intriguing mystery.
- Construction Techniques:
The construction techniques employed by the builders of Stonehenge are a testament to their engineering prowess. The transport of the massive stones over vast distances and their precise placement indicate a sophisticated understanding of physics and geometry. Theories vary on how the Neolithic people accomplished these feats, ranging from the use of sledges and ramps to a more complex system involving water transport. Nevertheless, the builders’ ingenuity and determination are evident in every stone.
- Alignments and Solstice Celebrations:
Stonehenge’s alignment with the solstices, particularly the summer and winter solstices, adds to its mystique. During these celestial events, the rising or setting sun aligns perfectly with specific stones, creating a spectacle of light and shadow. These alignments are believed to have held deep religious or cultural significance for the ancient people who built Stonehenge. Today, the site attracts thousands of visitors each year, especially during the summer solstice, when modern-day druids and pagans gather to celebrate the event.
- Conservation and Preservation:
Preserving Stonehenge for future generations is a priority for both the British government and conservation organizations. In recent years, efforts have been made to limit the impact of nearby roads and development on the monument. Visitors can explore the site through a carefully designed visitor center, which provides educational resources about the history and significance of Stonehenge. Conservation work and research continue to shed light on the mysteries surrounding this remarkable ancient monument.
Conclusion:
Stonehenge, with its enduring enigma, continues to amaze and fascinate us. Its ancient stones, rich in history and mystery, stand as a testament to the creativity and intelligence of our ancestors. As we explore the secrets of Stonehenge, we gain insights into the lives and beliefs of those who came before us. This remarkable monument invites us to reflect on the wonders of the past and serves as a timeless reminder of our connection to the ancient world.
![]()