Spirituality played a profound role in shaping the Indian freedom struggle, providing moral guidance, inner strength, and a unifying vision for the nation. Leaders of India’s independence movement often drew inspiration from spiritual principles, combining political activism with moral and ethical ideals. Spirituality helped the freedom fighters maintain resilience, purpose, and nonviolent approaches in the face of immense adversity.
Influence of Hindu Philosophy
Indian spiritual thought, especially teachings from the Vedas, Upanishads, and the Bhagavad Gita, deeply influenced the freedom movement. Leaders like Mahatma Gandhi interpreted the Gita’s message of selfless action and duty (karma yoga) to advocate for nonviolent resistance. The principle of performing one’s duty without attachment to results inspired countless Indians to participate in civil disobedience and peaceful protests while maintaining ethical integrity.
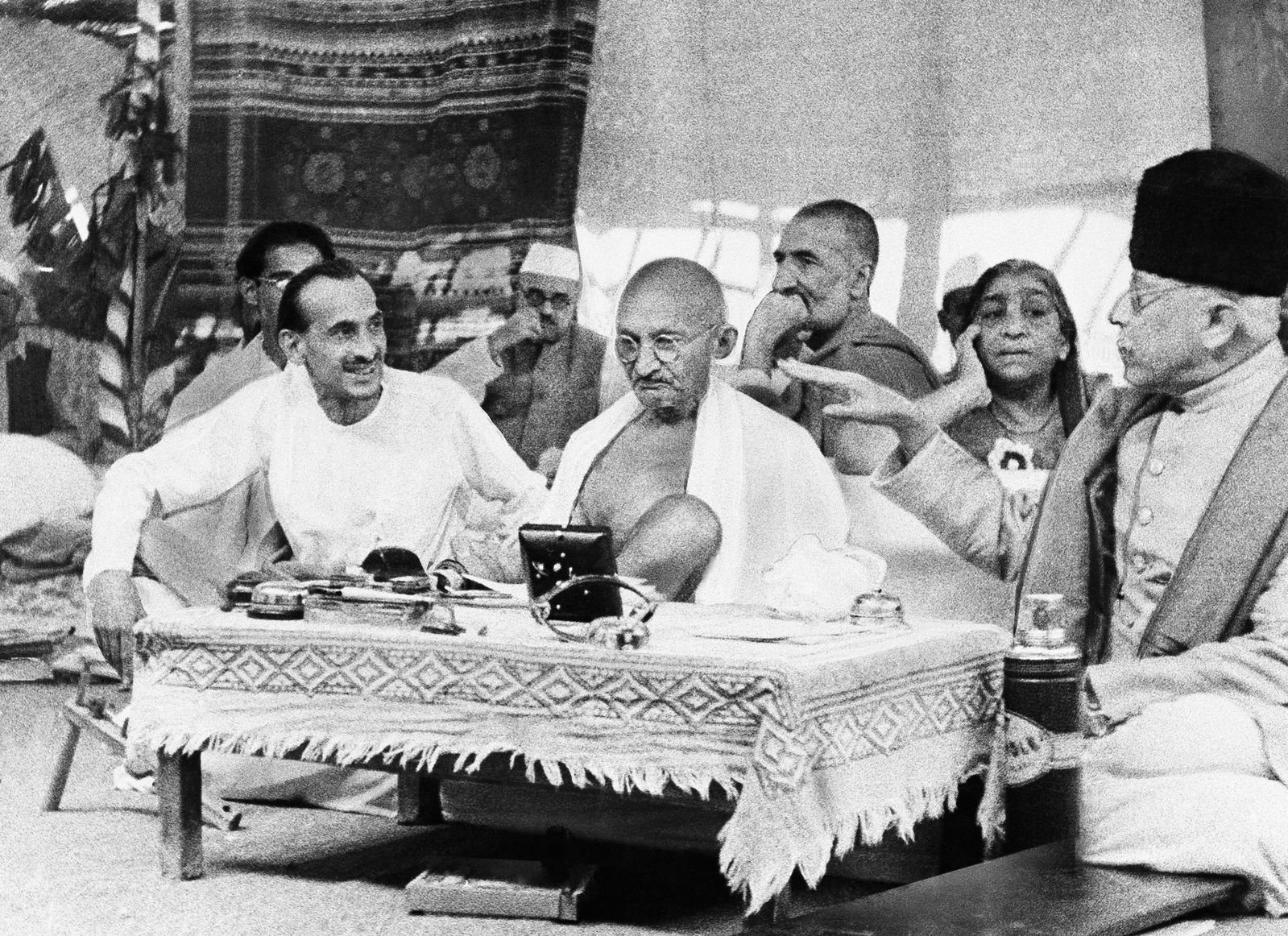
Mahatma Gandhi and Spirituality
Mahatma Gandhi is the most iconic figure in connecting spirituality with political activism. His philosophy of Satyagraha—truth-force or soul-force—was rooted in spiritual discipline and moral courage. Gandhi believed that inner purity and spiritual strength were essential for achieving social and political goals. Practices like fasting, meditation, and simplicity helped him cultivate self-control and inspire millions to join the struggle without resorting to violence.

Role of Other Spiritual Leaders
Besides Gandhi, other spiritual figures contributed to the freedom movement by promoting national consciousness and moral awakening. Swami Vivekananda’s call for youth empowerment, self-reliance, and service to the nation inspired many to work for India’s liberation. Similarly, leaders like Aurobindo Ghose combined spiritual ideals with political action, advocating for self-rule as part of a larger moral and spiritual mission.
Spiritual Values and National Unity
Spirituality also fostered unity among Indians of diverse religions, castes, and regions. The emphasis on universal values like truth, justice, compassion, and self-discipline helped build a cohesive vision for freedom. Spiritual teachings encouraged patience, moral courage, and self-sacrifice, which became the backbone of sustained movements like the Non-Cooperation and Quit India movements.
The Indian freedom struggle demonstrates that spirituality was not merely a private pursuit but a powerful source of social and political transformation. By integrating ethical principles, self-discipline, and moral courage into activism, spiritual ideals provided the strength and vision needed for India’s journey toward independence. The legacy of spirituality in the freedom movement continues to inspire ethical leadership and social responsibility in modern India.
Sadhguru Indian Philosopher and Mystic
![]()