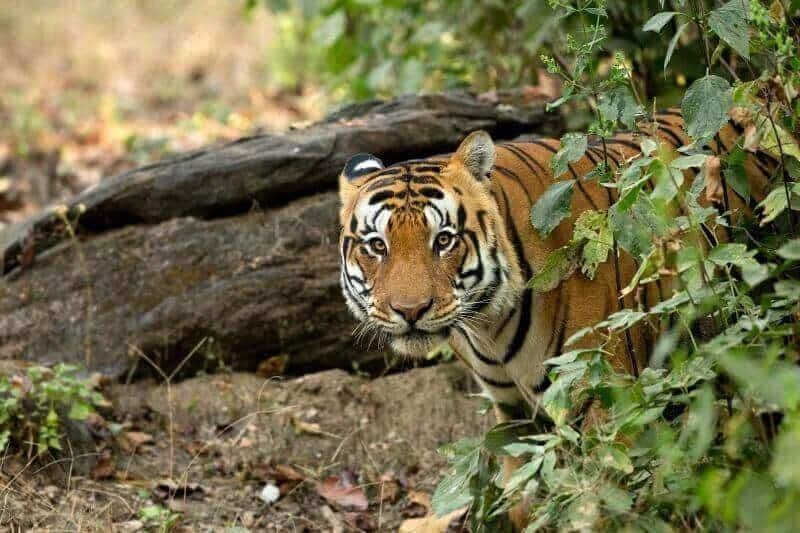
Tiger Reserve Forests in India: India is home to the largest population of tigers in the world, with an estimated 2,967 tigers in the wild. The Bengal tiger, India’s national animal, is found in different parts of the country, and it has become imperative to protect these magnificent creatures from habitat loss, poaching, and other threats. India has designated several tiger reserves forests to protect these tigers, and these reserves are now some of the most important protected areas for wildlife in India. In this article, we will explore the importance of these tiger reserve forests and their significance for tiger conservation in India.
Tiger Reserve Forests in India:
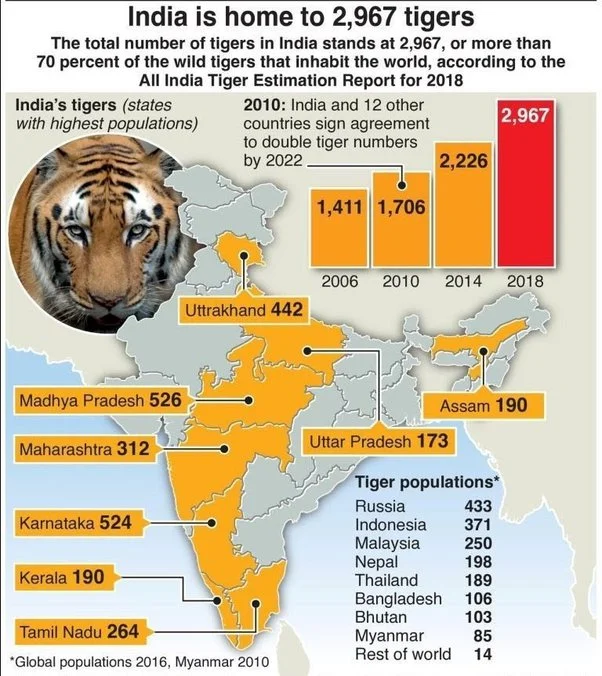
India has 51 tiger reserves, covering an area of over 71,000 square kilometers, which is approximately 2.2% of the country’s total land area. These reserves are spread across 18 states and are home to over 70% of the world’s tigers. The tiger reserves are managed by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and the respective state forest departments. The primary objective of these reserves is to provide a safe and secure environment for the Bengal tiger and its prey species.
The Tiger Reserve Forests:
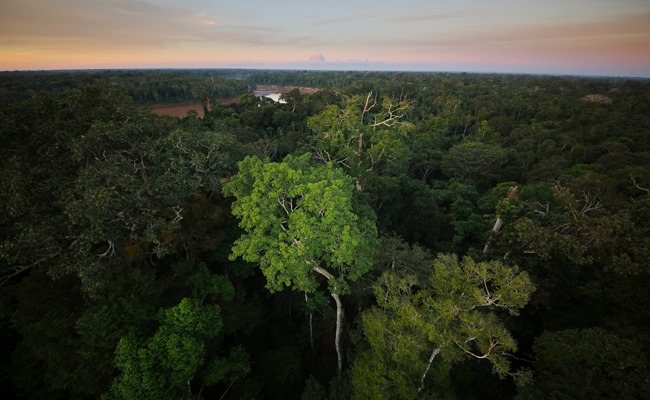
The tiger reserves in India are some of the most important protected areas for wildlife, and they play a crucial role in the conservation of the Bengal tiger. These reserves are also home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including several endangered species. The tiger reserves are usually large, contiguous areas of forests, which provide a safe and secure habitat for the tigers and their prey species. The forests in these reserves are managed to maintain the ecological balance of the area, ensuring that the tigers and other wildlife have a sustainable habitat.
Community Participation:
One of the significant factors that have contributed to the success of tiger conservation in India is community participation. The tiger reserves in India have involved local communities in the conservation efforts, which has helped to reduce human-wildlife conflict and poaching. The local communities are given incentives to protect the forests and wildlife, and they are also involved in eco-tourism activities, which provide them with an alternative livelihood. This approach has not only helped to conserve tigers but has also improved the socio-economic conditions of the local communities.
Challenges in Tiger Conservation:
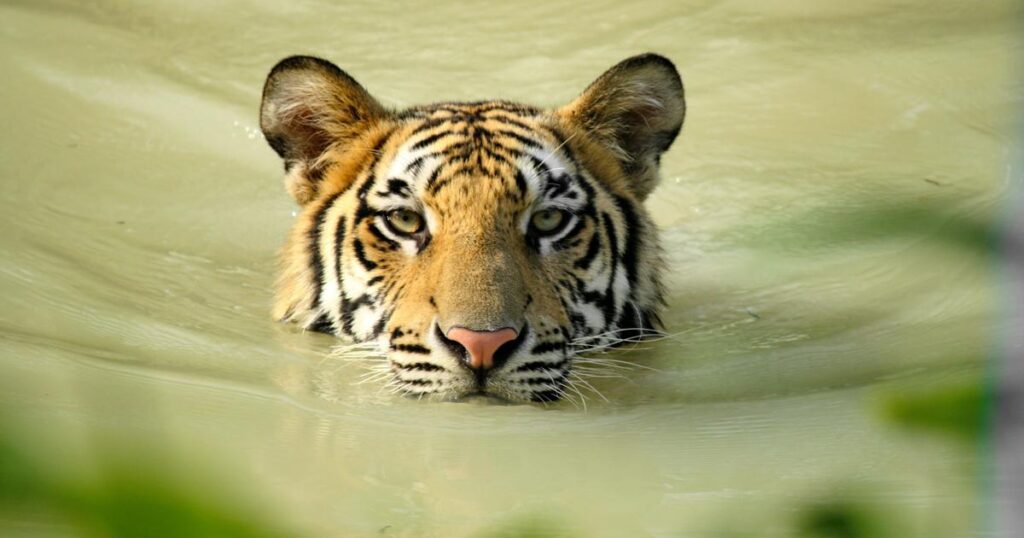

While the tiger reserves in India have been successful in conserving tigers, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed. Habitat loss due to deforestation, fragmentation of forested areas, and encroachment by human settlements are significant threats to tiger conservation. Poaching for tiger parts is also a significant challenge, and India has been working towards improving law enforcement to prevent poaching. Climate change is also a significant threat to the tiger’s habitat, and India needs to address this issue urgently.
The tiger reserve forests in India are crucial for the conservation of the Bengal tiger and other wildlife species. These reserves have been successful in protecting tigers and their habitat, and community participation has been a key factor in this success. However, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed, such as habitat loss, poaching, and climate change. India needs to continue its efforts to conserve tigers and their habitat, and the tiger reserves in India play a crucial role in this conservation effort.
Read Also: Kenya Masai Mara Forest Safari
![]()






One thought on “Tiger Reserve Forests in India”