Introduction:
Forests are an essential component of the Earth’s ecosystem, playing a crucial role in carbon sequestration and climate regulation. As climate change continues to pose significant challenges, understanding the importance of forests in mitigating its impacts becomes increasingly vital. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which forests contribute to carbon sequestration and climate regulation, highlighting their significance in tackling climate change.
- Forests as Carbon Sinks:
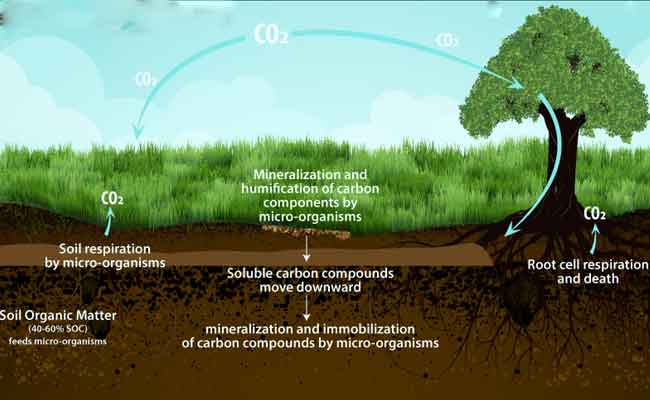
Forests are remarkable carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and storing it in trees, soil, and other organic matter. Trees utilize photosynthesis to convert CO2 into oxygen and carbon, with carbon being stored in various forms within the forest ecosystem. Through this process, forests act as crucial carbon reservoirs, reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Forest Cover and Carbon Storage:
The extent of forest cover directly affects carbon sequestration capabilities. Large, intact forests with diverse tree species have higher carbon storage capacities compared to fragmented or degraded forests. These intact ecosystems serve as vast reservoirs, sequestering significant amounts of carbon and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- Biodiversity and Climate Resilience:
Forests that harbor a wide array of plant and animal species contribute to climate resilience. Biodiversity within forests enhances their ability to withstand disturbances caused by climate change, such as extreme weather events and pest outbreaks. Diverse ecosystems are more resistant to disruption, maintaining their capacity for carbon sequestration and climate regulation.
- Forest Management and Carbon Sequestration:
Efficient forest management practices play a crucial role in maximizing carbon sequestration potential. Sustainable forestry approaches, such as reforestation and afforestation, can significantly contribute to carbon storage. These practices involve planting trees in deforested or degraded areas, enhancing the overall forest cover and carbon sequestration capacity.
- Avoided Deforestation and Emissions Reduction:
Halting deforestation and preserving existing forests is a key strategy for climate regulation. Deforestation accounts for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions, primarily due to the release of stored carbon when trees are cut down and burned. By preventing deforestation and promoting sustainable land use, forests can continue to sequester carbon and maintain their critical role in climate regulation.
- Forests and Water Cycle:
Forests also play a vital role in regulating the water cycle, which is intricately connected to climate patterns. Trees help maintain soil moisture levels, regulate evaporation, and promote rainfall. The presence of forests contributes to more stable hydrological patterns, reducing the risk of droughts and floods. These climate-related benefits further reinforce the importance of forest conservation and restoration.
- Forests and Air Quality:
In addition to carbon sequestration, forests also enhance air quality by acting as natural filters. Tree canopies absorb pollutants and particulate matter, reducing the concentration of harmful substances in the air. By improving air quality, forests contribute to human health and well-being, mitigating the adverse impacts of pollution on respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
- International Agreements and Forest Conservation:
Recognizing the critical role of forests in carbon sequestration and climate regulation, international agreements have been established to promote forest conservation. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+) initiative focus on reducing emissions from deforestation and promoting sustainable forest management, providing financial incentives for countries to protect their forests.
Conclusion:
Forests are invaluable allies in the fight against climate change. Their capacity to sequester carbon, regulate climate patterns, maintain biodiversity, and promote sustainable practices make them essential for a sustainable future.
![]()