The Potential of Green Infrastructure in Urban Planning and Design:
In recent years, the concept of green infrastructure has gained significant attention in the field of urban planning and design. Green infrastructure refers to the strategic integration of natural systems, such as parks, gardens, wetlands, and green roofs, into the urban fabric to enhance environmental sustainability, improve quality of life, and promote resilience. This article explores the potential benefits and challenges associated with green infrastructure in urban planning and design, highlighting its positive impact on various aspects of urban life.
I. Enhancing Environmental Sustainability:

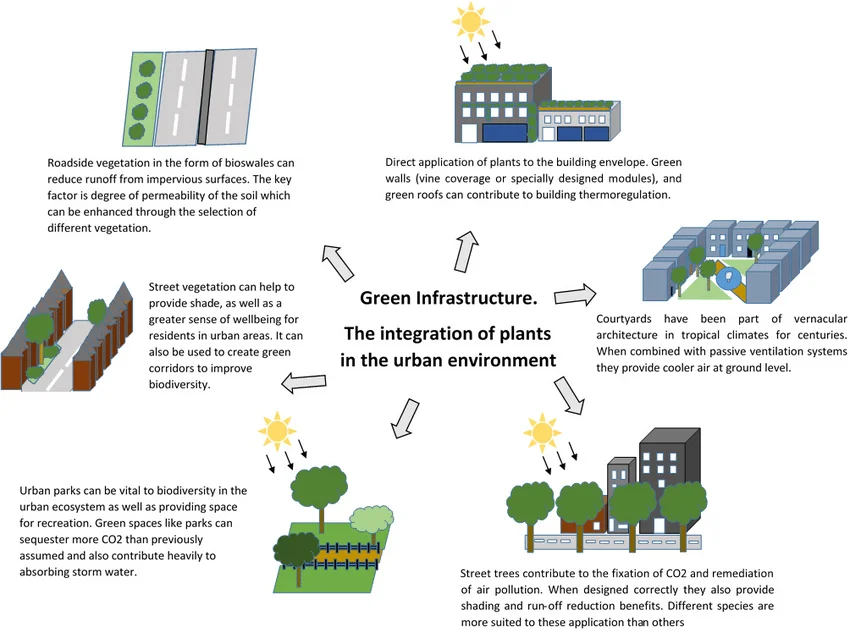
- Mitigating Urban Heat Island Effect: Green infrastructure offers a solution to the urban heat island effect, where cities experience higher temperatures due to the concentration of buildings and paved surfaces. The introduction of green spaces and vegetation helps to reduce heat buildup, improve air quality, and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change.
- Managing Stormwater: Traditional urban landscapes often suffer from inadequate stormwater management, leading to flooding and pollution of water bodies. Green infrastructure techniques, such as rain gardens, bioswales, and permeable pavements, can absorb and filter stormwater, reducing the burden on drainage systems and improving water quality.
II. Improving Quality of Life:
- Enhancing Physical and Mental Health: Access to green spaces has been linked to numerous physical and mental health benefits. Incorporating green infrastructure into urban planning provides opportunities for physical activities, relaxation, and stress reduction. Parks, community gardens, and tree-lined streets create a healthier and more pleasant living environment.
- Promoting Biodiversity and Ecological Connectivity: Green infrastructure contributes to the preservation and restoration of biodiversity in urban areas. By creating interconnected green spaces, wildlife corridors, and rooftop gardens, urban ecosystems can thrive, supporting a variety of plant and animal species. This ecological connectivity enhances urban resilience and fosters a sense of connection with nature.
III. Promoting Resilience:
- Climate Change Adaptation: Green infrastructure plays a vital role in adapting to climate change impacts, such as extreme weather events. Trees and vegetation provide shade, reducing energy consumption for cooling, while green roofs and walls offer insulation and reduce heat loss in winter. These measures increase the resilience of cities and contribute to climate change mitigation.
- Enhancing Social Cohesion: Green spaces act as social hubs, promoting community engagement, cohesion, and social interaction. Urban parks and plazas provide gathering spaces for cultural events, recreational activities, and community gardens, fostering a sense of belonging and strengthening social ties.
IV. Challenges and Considerations:
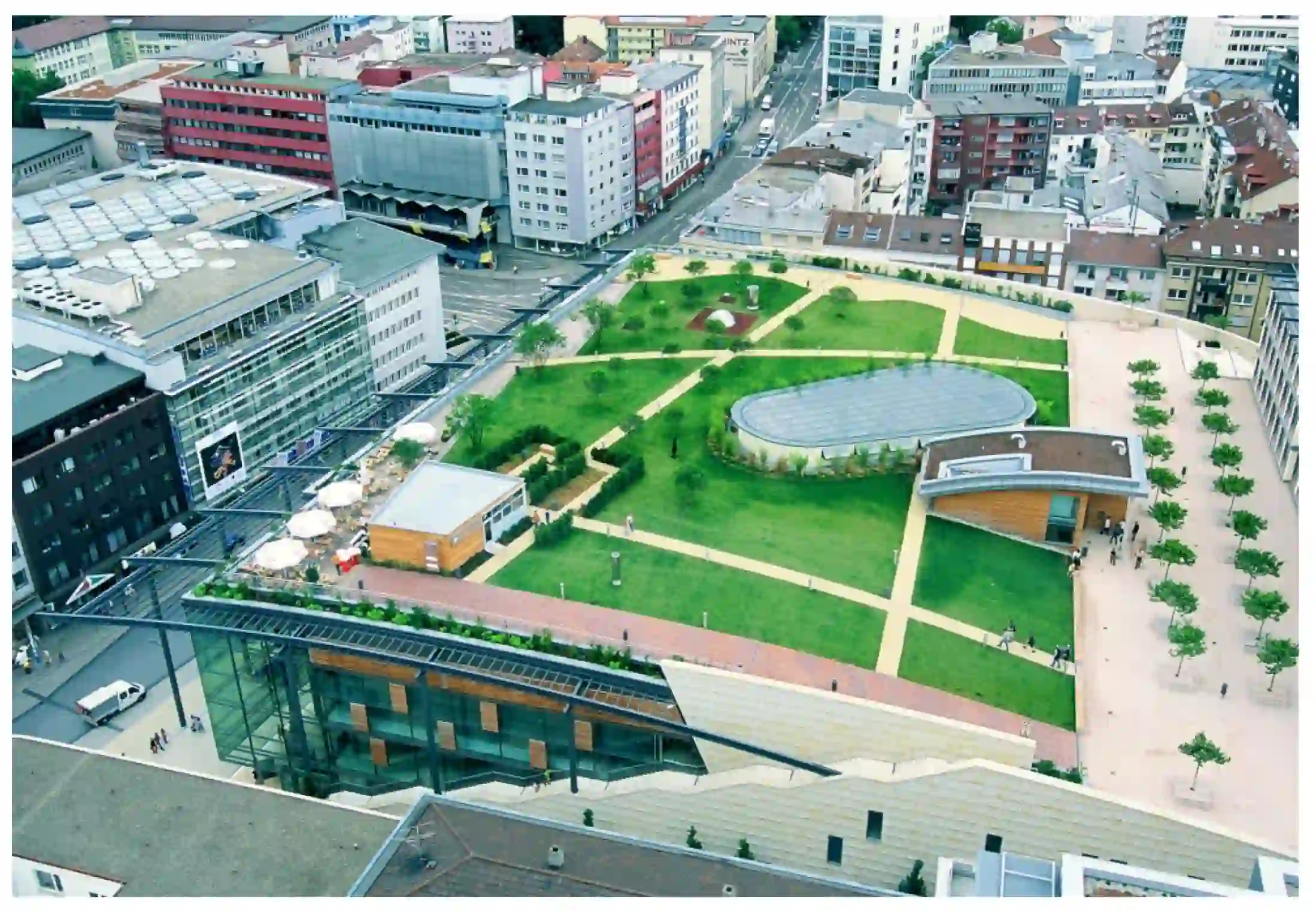
- Space Limitations: One of the key challenges in implementing green infrastructure is the limited availability of space in densely built urban areas. Creative design solutions, such as vertical gardens and rooftop parks, can help maximize the use of limited space and transform underutilized areas into green havens.
- Maintenance and Funding: Maintaining green infrastructure requires ongoing care, including irrigation, pruning, and pest control. Securing long-term funding for maintenance can be a hurdle for urban planners and local authorities. Innovative funding mechanisms, public-private partnerships, and community involvement can help overcome these challenges.
Green infrastructure presents a remarkable opportunity for urban planners and designers to create sustainable, resilient, and livable cities. By integrating nature into the built environment, cities can address pressing environmental challenges, improve quality of life, and create healthier, more vibrant communities. The potential benefits of green infrastructure are vast, but it is crucial to consider the associated challenges and implement innovative strategies to overcome them. With careful planning and collaboration, green infrastructure can transform our urban landscapes into thriving, sustainable environments for generations to come.
Read Also: Water Scarcity
![]()






One thought on “The Potential of Green Infrastructure in Urban Planning and Design”