Although the terms World Wide Web and Internet are often used synonymously, they are distinct. Over the years, the gap between the Internet and the Web has grown wider, and today they represent two very different layers of the digital world. While the Internet is the underlying infrastructure, the Web is just one of the many services running on top of it. As technology evolves, this separation has become even more noticeable.
What Is the Internet?
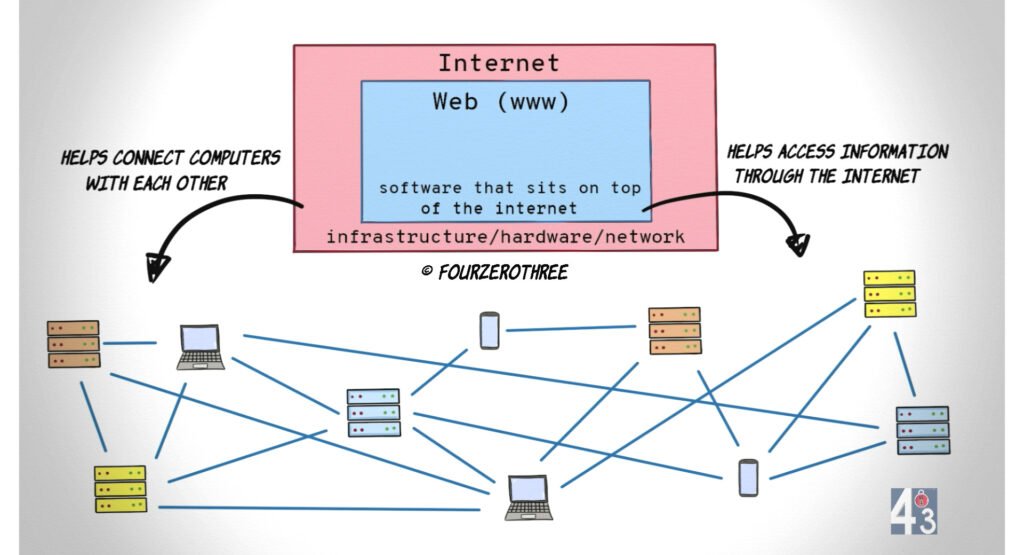
The Internet is a worldwide network of linked computers and servers. It is the backbone that allows data to travel from one device to another using standardized protocols like TCP/IP. The Internet itself does not contain websites, images, or videos. Instead, it provides the pathways that allow data to move across the world.
Email, file transfers (FTP), online gaming, cloud computing, and messaging services all rely on the Internet. These services do not necessarily depend on the World Wide Web to function. This foundational role of the Internet has remained consistent, even as new technologies continue to emerge.
What Is the World Wide Web?
The World Wide Web is a service that runs over the Internet. It consists of websites, web pages, and web applications that are accessed using browsers like Chrome, Firefox, or Safari. The Web relies on technologies such as HTTP, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to display content.
In simple terms, if the Internet is the road system, the Web is one type of vehicle traveling on those roads. Social media platforms, blogs, news sites, and e-commerce stores all belong to the Web, but they are only a fraction of what the Internet supports.
How the Internet and the Web Drifted Apart
In the early days, the Web was the most visible and dominant use of the Internet. However, as digital innovation accelerated, many Internet-based services began operating independently of traditional web browsers. Mobile apps, IoT devices, APIs, and streaming services often use the Internet without relying heavily on the Web.
For example, when you use a mobile banking app or stream content on a smart TV, you are using the Internet, but not necessarily browsing the Web. This shift has caused the Internet and the Web to drift further apart in terms of usage, design, and purpose.
The Rise of Apps, APIs, and Cloud Services
One major reason for this growing separation is the rise of mobile applications and APIs. Apps communicate directly with servers through APIs, bypassing traditional web pages. Cloud services, microservices architecture, and real-time data processing rely more on backend Internet communication than on front-end web interfaces.
Additionally, technologies like blockchain, edge computing, and IoT devices depend heavily on Internet connectivity while having little or no connection to the World Wide Web.
Why This Separation Matters
Understanding the difference between the Internet and the Web is important for businesses, developers, and users. For developers, it influences how applications are built and optimized. For businesses, it affects digital strategy, cybersecurity planning, and scalability. For users, it explains why not all online experiences happen inside a browser.
As the Internet continues to evolve, innovation is increasingly happening beyond the traditional Web, shaping a more diverse and complex digital ecosystem.
The Internet and the World Wide Web are more distinct today than ever before. While the Internet continues to expand as a global communication infrastructure, the Web is just one of many services built upon it. As apps, devices, and services grow beyond browser-based experiences, the gap between the two will likely widen even further. Recognizing this difference helps us better understand the future of technology and the digital world we rely on every day.
Effects of AI in Upcoming Technology
Manhole – Essential Access Points in Urban Infrastructure
RCPC Manhole Covers and Frames
Read Also: Social Network Website Design
![]()