Introduction
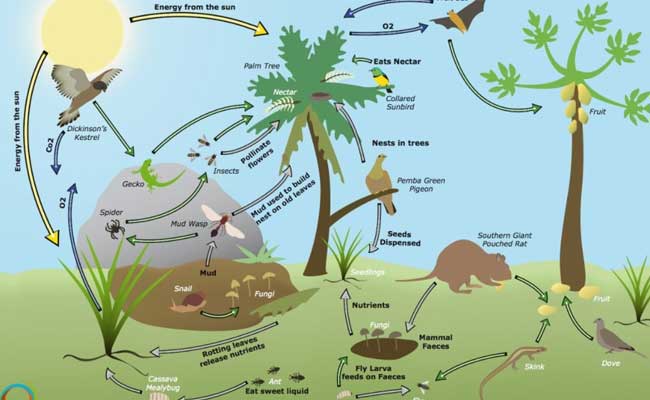
Biodiversity, the incredible variety of life on Earth, is a fundamental component of our planet’s ecosystems. It encompasses all living organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, as well as the intricate web of interactions between them. Biodiversity plays a critical role in sustaining ecosystems, providing numerous benefits that are essential for the survival and well-being of both wildlife and humanity. In this article, we explore the importance of biodiversity and its impact on the functioning and resilience of ecosystems.
I. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Stability
Biodiversity is closely linked to the stability of ecosystems. A diverse range of species within an ecosystem creates a balance that ensures its proper functioning. Each organism has a unique role to play, contributing to various ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control. The loss of even a single species can disrupt these delicate interactions, leading to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
II. Ecosystem Services
Biodiversity provides a wide array of services that are essential for human well-being. These ecosystem services include the provision of food, clean water, and air, as well as the regulation of climate, disease control, and natural resources such as timber and fuel. Without biodiversity, these services would be compromised, jeopardizing our ability to meet our basic needs and maintain a sustainable society.
III. Resilience and Adaptability
Ecosystems with high biodiversity are more resilient and adaptable to environmental changes. When faced with disturbances such as natural disasters or climate change, diverse ecosystems have a greater capacity to recover and maintain their functionality. The presence of various species with different traits and abilities ensures that some organisms can withstand and adapt to changing conditions, preventing ecosystem collapse.
IV. Genetic Diversity
Biodiversity also encompasses genetic diversity within species. Genetic variation provides the basis for adaptation and evolution, enabling species to survive in changing environments. This diversity acts as a buffer against diseases, pests, and other threats that can decimate populations. It also plays a crucial role in crop improvement, as genetic resources from wild relatives can be used to develop more resilient and productive cultivars.
V. Cultural and Aesthetic Value
Beyond its ecological and utilitarian importance, biodiversity holds significant cultural and aesthetic value. It is intricately woven into the fabric of human cultures, providing inspiration for art, literature, and traditional practices. Indigenous peoples, for example, rely on biodiversity for their spiritual beliefs, traditional medicine, and sustenance. Preserving biodiversity ensures the continuity of cultural heritage and enriches our lives with beauty and diversity.
VI. Threats to Biodiversity
Unfortunately, biodiversity is under threat due to human activities. Habitat destruction, pollution, overexploitation of resources, and climate change are major drivers of biodiversity loss. The destruction of natural habitats not only eliminates species directly but also fragments ecosystems, reducing their ability to support diverse life forms. Urgent action is needed to address these threats and conserve biodiversity for the benefit of present and future generations.
VII. Conservation Strategies
Conservation efforts are crucial for preserving biodiversity and sustaining ecosystems. Protected areas, such as national parks and reserves, play a vital role in safeguarding habitats and species. Additionally, sustainable land and resource management practices can minimize the impact of human activities on biodiversity. Conservation organizations, governments, and individuals must work together to promote awareness, implement effective policies, and support initiatives that prioritize biodiversity conservation.
Conclusion
Biodiversity is the foundation of life on Earth, and its preservation is essential for the long-term health and sustainability of ecosystems. The interdependence between species and their environment highlights the intricate web of life that we must protect. By recognizing the importance of biodiversity and taking action to conserve it, we can ensure the continued provision of vital
![]()