Understanding Schizophrenia: Unraveling the Complexities of a Mental Disorder
Introduction: Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects approximately 20 million people worldwide. It is characterized by a disconnection from reality, altered perceptions, and abnormal social behaviors. Despite extensive research, the causes of schizophrenia remain elusive, and its symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of schizophrenia, exploring its symptoms, potential causes, and available treatments.
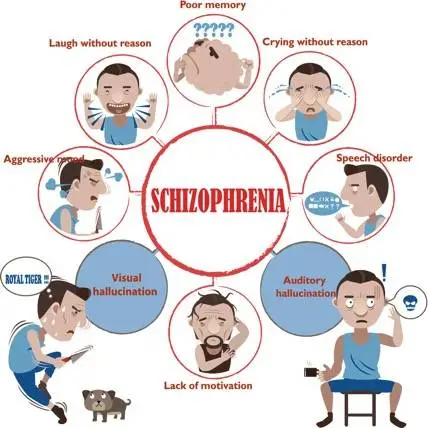
- The Symptoms of Schizophrenia: Schizophrenia is a complex disorder with a wide range of symptoms that can vary from person to person. The most common symptoms can be categorized into three groups: positive symptoms, negative symptoms, and cognitive symptoms.
a. Positive Symptoms: Positive symptoms refer to the presence of abnormal experiences that are not typically observed in healthy individuals. These include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and speech, and heightened or exaggerated emotions.
b. Negative Symptoms: Negative symptoms involve a lack or decrease in normal emotional and behavioral functions. These symptoms may manifest as social withdrawal, reduced motivation, decreased ability to experience pleasure, and difficulties with speech and expression.
c. Cognitive Symptoms: Cognitive symptoms affect the individual’s thinking processes and their ability to understand and make sense of information. These symptoms can include problems with attention, memory, and decision-making.
- Potential Causes of Schizophrenia: The exact causes of schizophrenia remain unknown, but research suggests a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurochemical factors contribute to its development.
a. Genetic Factors: Studies have shown that schizophrenia tends to run in families, indicating a genetic component. However, no single gene has been identified as the sole cause of the disorder. Instead, it is believed that multiple genes, each with small effects, interact with environmental factors to increase the risk of developing schizophrenia.
b. Environmental Factors: Certain environmental factors may contribute to the development of schizophrenia, such as exposure to viruses or malnutrition during fetal development, complications during childbirth, and psychosocial stressors during childhood or adolescence.
c. Neurochemical Imbalances: Schizophrenia is associated with imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and glutamate. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in regulating brain function and may contribute to the onset of symptoms when disrupted.
- Treatment and Management: While there is currently no cure for schizophrenia, treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with the disorder.
a. Medication: Antipsychotic medications are the primary treatment for schizophrenia. These medications help alleviate the positive symptoms by targeting the imbalances in brain neurotransmitters. However, they may have side effects, and finding the right medication and dosage can be a trial-and-error process.
b. Psychotherapy: Psychosocial interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy, can complement medication by helping individuals cope with symptoms, improve social skills, and enhance problem-solving abilities.
c. Supportive Services: Supportive services, such as vocational rehabilitation, housing assistance, and community support programs, can greatly benefit individuals with schizophrenia by providing them with the necessary tools and resources to lead fulfilling lives.
Conclusion: Schizophrenia is a complex and challenging disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Through further research and advancements in understanding its underlying mechanisms, we hope to develop more effective treatments and interventions. By raising awareness and promoting acceptance, we can reduce the stigma surrounding schizophrenia and support individuals in their journey towards recovery and improved quality of life.
![]()