Psychological Theories: Psychological theories provide us with invaluable insights into the intricate workings of the human mind. They help us understand the complexities of human behavior, emotions, cognition, and development. In this article, we will delve into some of the most prominent psychological theories, shedding light on their key concepts and contributions to our understanding of the human psyche.
Psychoanalytic Theory:

Developed by Sigmund Freud, psychoanalytic theory suggests that human behavior is influenced by unconscious drives, instincts, and childhood experiences. According to Freud, the mind is divided into three parts: the id (basic instincts and desires), the ego (mediates between the id and the external world), and the superego (internalized moral standards). This theory highlights the significance of early childhood experiences and the role of the unconscious mind in shaping our behavior.
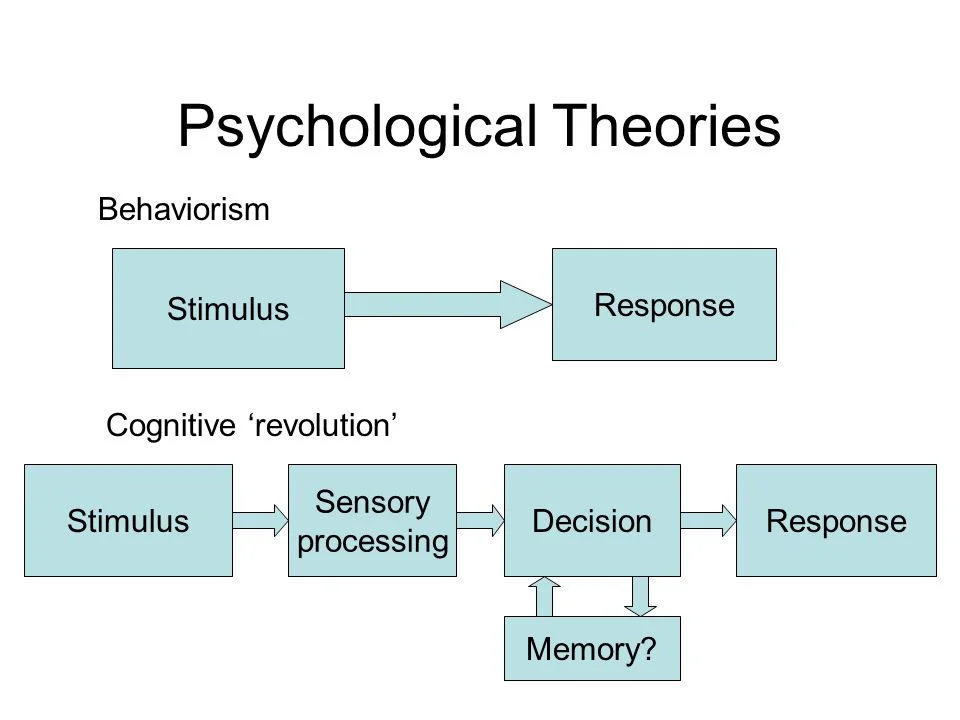
Behaviorism:
Behaviorism, pioneered by B.F. Skinner and John B. Watson, focuses on observable behavior rather than internal mental processes. It emphasizes the influence of the environment and reinforcement on shaping behavior. Behaviorists believe that learning occurs through the association of stimuli and rewards or punishments. This theory has had a profound impact on fields such as education, therapy, and behavior modification.
Cognitive Theory:
Cognitive theory explores how people perceive, process, and store information. Developed by Jean Piaget and Albert Bandura, this theory emphasizes the role of mental processes in understanding human behavior. It highlights concepts such as attention, memory, problem-solving, and language acquisition. Cognitive theories have greatly influenced fields such as education, cognitive psychology, and artificial intelligence.
Humanistic Theory:
Humanistic theories, including those by Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow, focus on the inherent goodness and potential for growth in individuals. These theories emphasize the importance of self-actualization, personal agency, and subjective experiences. Humanistic psychology has greatly influenced areas such as counseling, positive psychology, and self-help movements.
Socio-Cultural Theory:

Socio-cultural theory, developed by Lev Vygotsky, emphasizes the role of culture and social interactions in shaping cognitive development. It highlights the importance of social learning, language, and cultural tools in acquiring knowledge and understanding the world. This theory has significant implications for education, cross-cultural psychology, and understanding the impact of social factors on individual development.
Evolutionary Theory:
Evolutionary psychology explores how psychological traits and behaviors have evolved through natural selection. It suggests that certain behaviors and cognitive processes are adaptive and have helped humans survive and reproduce over time. This theory sheds light on topics such as mate selection, parental investment, and aggression. Evolutionary psychology has influenced fields such as social psychology, behavioral genetics, and anthropology.
Psychological theories offer valuable frameworks for understanding the intricacies of the human mind. From psychoanalytic theory to behaviorism, cognitive theory, humanistic theory, socio-cultural theory, and evolutionary theory, each perspective contributes unique insights into various aspects of human behavior and cognition. By exploring these theories, we gain a deeper appreciation of the complexity and diversity of human nature. These theories continue to shape the field of psychology, guiding research and practical applications in numerous domains, including therapy, education, and social interventions.
Read Also: Stress Management Techniques
![]()





One thought on “Psychological Theories”