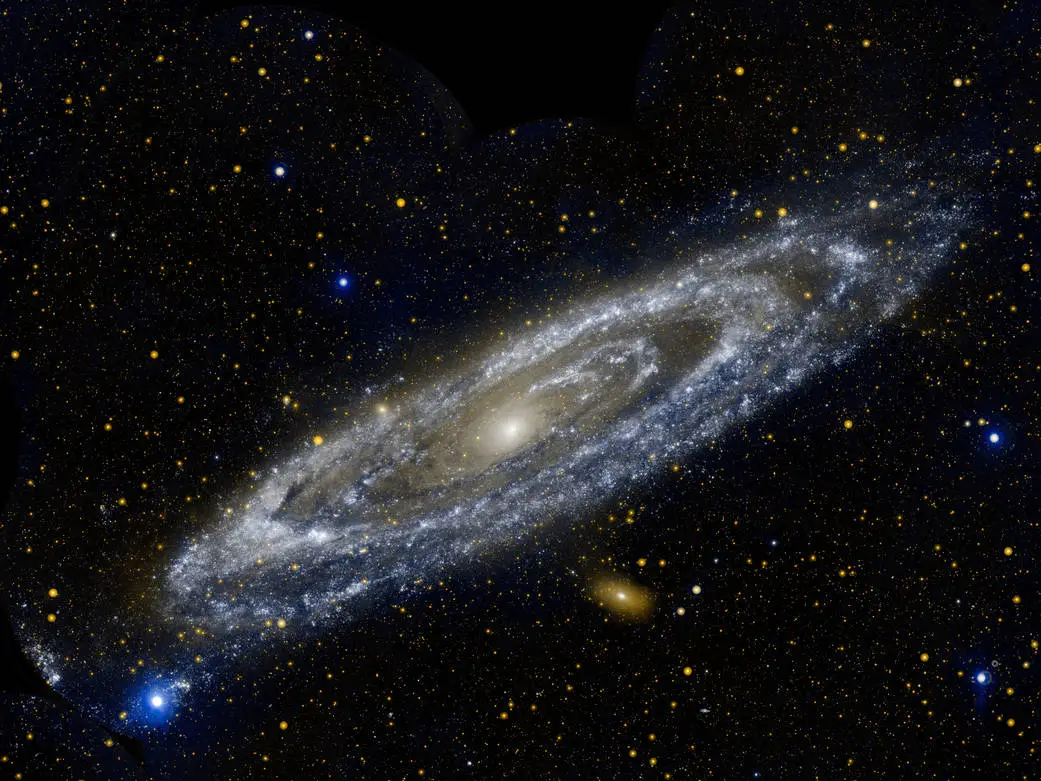
Galaxies, vast collections of stars, planets, dust, and dark matter, have fascinated astronomers and stargazers for centuries. From the elegant spiral arms of the Milky Way to the mysterious irregular shapes of distant galaxies, these cosmic structures hold secrets that continue to intrigue scientists. Understanding galaxies not only helps us explore the universe but also gives insight into the origins of our own existence.
What Are Galaxies?
A galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars, stellar remnants, gas, dust, and dark matter. They come in various shapes and sizes, ranging from dwarf galaxies with only a few billion stars to giant ellipticals with trillions. The most familiar types of galaxies include spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies, each with unique features and mysteries.
- Spiral Galaxies: Known for their rotating arms, spiral galaxies like the Milky Way contain a mix of young and old stars, gas, and dust.
- Elliptical Galaxies: These are more rounded and contain older stars, often lacking significant new star formation.
- Irregular Galaxies: These chaotic galaxies defy typical structures, often influenced by gravitational interactions with other galaxies.
The Role of Dark Matter in Galaxies
One of the greatest mysteries surrounding galaxies is the role of dark matter. Scientists estimate that more than 80% of a galaxy’s mass is invisible, composed of dark matter that neither emits nor absorbs light. Dark matter plays a crucial role in holding galaxies together, influencing their rotation and evolution. Without it, galaxies as we know them could not exist.
Galactic Collisions: Cosmic Ballets
Galaxies are not isolated; they interact and even collide in a slow cosmic dance. These galactic collisions can trigger intense star formation, distort shapes, and create spectacular structures like tidal tails. Observing these collisions helps astronomers understand how galaxies grow, merge, and evolve over billions of years. The Milky Way itself is on a collision course with the Andromeda Galaxy, an event expected to occur in about 4 billion years.
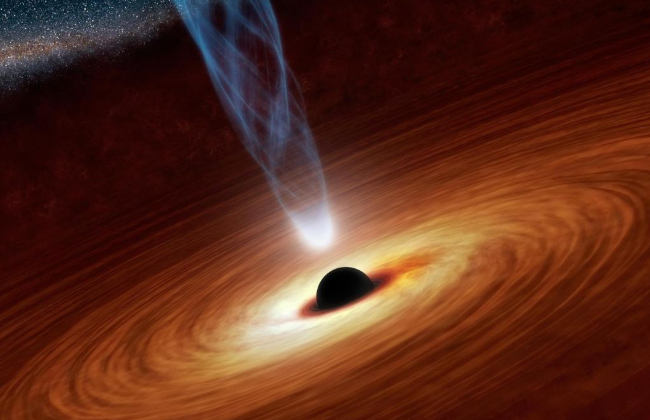
Black Holes at the Heart of Galaxies
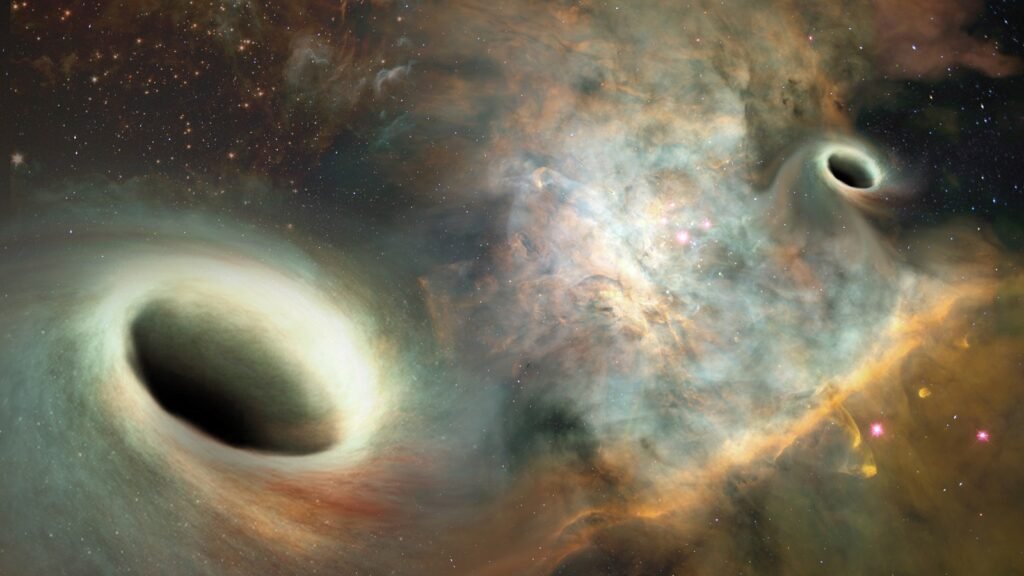

Almost every large galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole at its center. These cosmic giants, millions to billions of times more massive than our Sun, influence the formation of stars and the dynamics of their host galaxy. The energy released by matter falling into black holes, often observed as quasars, provides crucial clues about galaxy evolution.
The Search for Galactic Origins
Understanding the origin of galaxies is a central quest in cosmology. The prevailing theory, the Big Bang, suggests that galaxies formed from primordial fluctuations in the early universe. Over billions of years, gravity pulled matter together, forming stars, clusters, and eventually the galaxies we observe today. Despite decades of research, the early stages of galaxy formation remain shrouded in mystery.
Why Studying Galaxies Matters
Studying galaxies offers more than just knowledge of distant stars. It helps answer fundamental questions: How did the universe evolve? What is the fate of cosmic structures? Are there conditions suitable for life beyond Earth? By studying galaxies, astronomers also refine models of dark matter, dark energy, and the overall expansion of the universe.
Galaxies are not just beautiful cosmic structures—they are the key to understanding the universe itself. From dark matter to supermassive black holes, each discovery uncovers new layers of mystery. As telescopes become more advanced and space exploration continues, we edge closer to unveiling the secrets of these celestial giants. The mystery of galaxies is far from solved, but every observation brings us closer to comprehending our place in the cosmos.
Discover the Best Telescopes for Amateur Astronomers
Read Also: Education Website Design
![]()