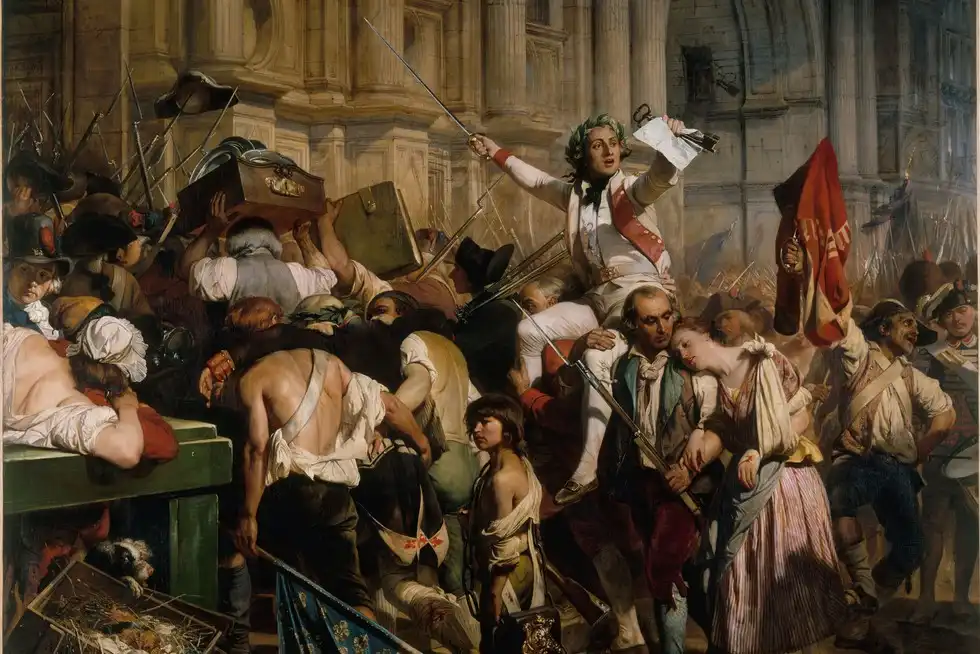
French Revolution: The French Revolution, which lasted from 1789 to 1799, was a monumental event that reshaped the political and social landscape of France and influenced the course of world history. It marked the fall of absolute monarchy, the rise of democratic ideals and the birth of modern nationalism. The revolution’s impact on law, society and governance continues to resonate today, influencing movements for freedom and equality worldwide. Below, we explore the key aspects that underline the significance of the French Revolution.
1. End of absolute monarchy:
Before the French Revolution, France was ruled by an absolute monarchy under Louis XVI. The king had full control over the government and the public had no say in government affairs. The revolution radically changed this structure by abolishing the monarchy and paving the way for a democratic society.
The fall of the kingdom symbolized the dissolution of divine and hereditary authority. It also marked the rise of sovereignty, where power came from the people rather than being handed down through the blood of the king. This change not only affected France, but inspired other countries to challenge their sovereignty, as it was a very important change in the history of the state.
2. Birth of Republic and Democratic ideals:
One of the most important contributions of the French Revolution was the birth of the French Republic. In 1792, the National Convention formally abolished the monarchy and declared France a republic. This declaration of a republic echoed the democratic ideals of liberty, equality and fraternity, which became the guiding principles of the revolution. These ideals were enshrined in the Constitution of 1793, which granted universal male suffrage and aimed to create a more just and equitable society.
The French Revolution set a powerful example for democratic movements in Europe and around the world. It provided a blueprint for future revolutions that sought to overthrow tyrannical regimes and establish governments that reflected the will of the people.
3. Social Reforms and Fall of Feudalism:

The French Revolution played an important role in dismantling the feudal system that had dominated France for centuries. The ancient regime, based on aristocratic privilege and social stratification, was overthrown during the revolution. Privileges of the nobility, such as tax exemptions and special legal rights, were abolished. In their place, new laws were enacted to ensure greater equality among citizens.
The revolution empowered the common people, especially the middle and lower classes, who were previously excluded from political decision-making. The National Assembly introduced several reforms, including the abolition of feudal dues, redistribution of land, and the creation of a more merit-based society. This leveling of the social playing field was instrumental in promoting social mobility and changing the rigid class structure that defined France.
4. Rise of Nationalism:
Nationalism, the idea of strong identification with and pride in a nation, took root during the French Revolution. As the Revolution progressed, the concept of citizenship became central to French identity. Revolutionaries encouraged people to see themselves as members of a nation, bound together by common ideals and values rather than loyalty to a king or elite.
This rise of nationalism also had a profound impact on world politics. Other countries observed how the French rallied around the idea of a unified nation, leading to nationalist movements in Europe, Latin America, and beyond. The French Revolution proved that ordinary people could not only take control of their government but also reshape their national identity.
5. The reign of terror and its lessons:
Despite its ideals, the French Revolution gave rise to one of the most infamous periods in world history: the Reign of Terror. From 1793 to 1794, radical revolutionaries led by Maximilien Robespierre launched extreme violence and repression to eliminate perceived enemies of the revolution. Thousands were executed by guillotine, including King Louis XVI and Queen Marie Antoinette.
Reign of Terror has served as a cautionary tale about the dangers of political extremism. It highlights the need for balance in revolutionary movements and emphasizes the importance of protecting individual rights even in the pursuit of larger social change. Although a dark period in the history of the revolution, it left an important lesson about the limits of power and the importance of protecting civil liberties.
6. Long-lasting global impact:
The significance of the French Revolution extended far beyond the borders of France. Its ideas inspired countless other movements for democracy and social justice around the world. The American Revolution may have happened before, but the French Revolution gave the world a detailed and lasting example of how people could overthrow an entrenched regime and rebuild their society.
Colonies in Europe, Latin America, and even Africa and Asia looked to the French Revolution as a model for freedom from oppression. Whether it was the struggle for freedom, the abolition of slavery or the push for women’s rights, the ideals of the French Revolution resonate even today.
The French Revolution was a defining moment in human history, marking the transition from feudalism to modern democracy. Its influence on political thought, social reform and national identity continues to shape societies today. Challenging the status quo and promoting ideals of liberty, equality and fraternity, the revolution remains a symbol of human resilience and the ongoing struggle for justice.
Read Also: Industrial Revolution
![]()






3 thoughts on “French Revolution”