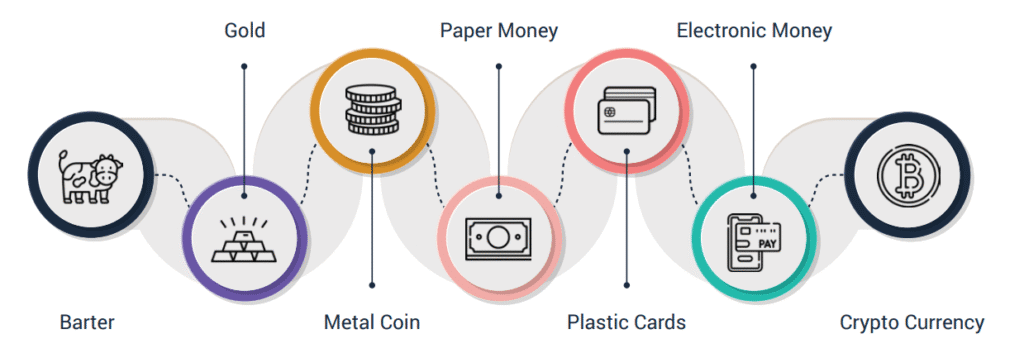
The history of human civilization is closely tied to the way people exchange goods and services. Long before the invention of coins and currency, societies relied on a system known as barter. This was the earliest form of trade, where one commodity was exchanged directly for another. For instance, a farmer might trade a sack of rice with a potter in exchange for clay pots. The barter system was simple, but it had limitations that eventually led to the creation of money.
The Limitations of the Barter System
Although barter played a vital role in early communities, it was not always practical. One major issue was the “double coincidence of wants.” Both parties had to desire what the other offered at the same time, which made transactions difficult. For example, if a shepherd wanted clothes but the weaver did not need wool, the trade could not occur. The absence of a standardized method of determining worth was another disadvantage. It was hard to determine how many fish were equal to a piece of jewelry or a tool. Moreover, goods like grain or livestock were perishable, making them unsuitable for long-term storage of value. These challenges highlighted the need for a more efficient system of exchange.
Emergence of Money
To overcome these difficulties, societies gradually shifted towards the use of money. The earliest forms of money included commodities such as salt, cattle, shells, or precious metals, which were widely accepted and held value. Over time, metal coins emerged because they were durable, divisible, and easy to transport. Ancient civilizations like the Mesopotamians and Greeks used silver and gold coins as standardized mediums of exchange.
Paper Money and Modern Currency
Carrying around big amounts of metal money became a nuisance as commerce increased. This led to the introduction of paper money, first seen in China during the Tang Dynasty and later adopted worldwide. Banks and governments began issuing currency backed by gold or silver reserves, ensuring trust and stability. With time, economies moved toward fiat money—currency that holds value because people trust the authority that issues it, not because it is backed by precious metals.
The journey from barter to money represents a significant step in human progress. While the barter system laid the foundation of trade, the invention of money revolutionized economies by providing a universal medium of exchange, a measure of value, and a store of wealth. Today, with the rise of digital payments and cryptocurrencies, the concept of money continues to evolve, reflecting humanity’s constant search for convenience and efficiency in exchange.
Restaurants and Cafes Business Idea
Professional Investment Website
![]()





