Edge Computing: The Future of Data Processing and Storage
In today’s world, the amount of data being generated and processed is growing exponentially. To cope with this explosion in data, traditional cloud computing infrastructure is no longer sufficient. Edge computing, a distributed computing paradigm, is emerging as the solution to handle this growing data demand. In this article, we will explore what edge computing is, how it works, and its potential benefits.
What is Edge Computing?
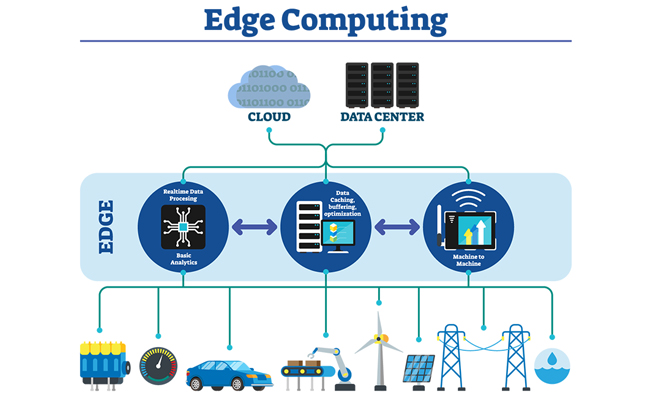
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that processes and stores data closer to the source of the data, rather than in a centralized cloud. In other words, instead of processing and storing data in a distant data center, edge computing brings the processing and storage capabilities closer to the edge of the network, where data is being generated.
Edge computing can be thought of as a way to extend cloud computing services to the edge of the network, such as sensors, devices, and other IoT (Internet of Things) endpoints. This enables faster processing of data, real-time data analysis, and reduces latency, making it ideal for applications that require immediate responses.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge computing works by deploying edge nodes, which are small computing devices that are placed close to the source of data. These edge nodes can be anything from small computers to sensors, and they are connected to the cloud or data center through the network.
The edge nodes process the data that they receive from the source and send only the relevant data to the cloud or data center for further analysis and storage. This approach reduces the amount of data that needs to be sent over the network, which reduces network congestion and improves response times.
Benefits of Edge Computing
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing enables faster processing of data as it brings the computing power closer to the source of the data. This reduces the time it takes to transmit data to a data center or cloud, reducing latency and enabling real-time processing.
- Improved Security: Edge computing can provide an additional layer of security by processing and storing sensitive data locally, rather than sending it over the network. This makes it more difficult for hackers to access and steal data.
- Reduced Network Congestion: Edge computing reduces the amount of data that needs to be sent over the network, reducing network congestion and improving overall network performance.
- Cost Savings: Edge computing reduces the cost of sending data to a central data center or cloud. This is because less data needs to be sent, and the cost of sending data over long distances is reduced.
- Scalability: Edge computing enables organizations to scale their computing resources more easily, as edge nodes can be easily deployed as needed. This makes it easier to handle peak workloads and spikes in demand.
Applications of Edge Computing
- IoT (Internet of Things): Edge computing is ideal for IoT applications, as it enables faster processing of data, real-time analysis, and reduces latency.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing can be used to enable real-time decision making in autonomous vehicles, such as self-driving cars.
- Healthcare: Edge computing can be used to enable real-time monitoring of patients, reducing the need for hospitalization and enabling better patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing: Edge computing can be used to enable real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency.
Conclusion
Edge computing is emerging as the solution to handle the growing demand for data processing and storage. By bringing the processing and storage capabilities closer to the source of the data, edge computing reduces latency, improves security, and reduces network congestion. It also enables real-time processing and analysis of data, making it ideal for applications that require immediate responses. As more and more devices become connected to the Internet, edge computing will play an increasingly important role in enabling the next generation of IoT applications.
![]()