Darwin’s Evolution Theory: Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution, published in his book “On the Origin of Species” in 1859, revolutionized the way we understand the natural world. Darwin’s ideas were not universally accepted at the time, but they have since become a cornerstone of modern biology. This article will explore the key concepts of Darwin’s theory of evolution and their implications for our understanding of life on Earth.
The Origin of Species:

Darwin’s theory of evolution is based on the idea that all living things are descended from a common ancestor. This ancestor, which Darwin called the “primordial form,” was a simple, single-celled organism that existed billions of years ago. Over time, this organism evolved and diversified, eventually giving rise to the vast array of life we see today.
One of the key mechanisms driving this evolution is natural selection. Natural selection is the process by which certain traits become more common in a population over time, because individuals with those traits are better able to survive and reproduce. For example, imagine a population of birds that live on an island with two types of seeds: small seeds and large seeds. Birds with larger beaks are better able to crack open the large seeds, while birds with smaller beaks are better able to eat the small seeds. Over time, the population will come to be dominated by birds with beak sizes that are well-suited to the available food sources.
Evolution and Adaptation:
Evolution by natural selection leads to the development of adaptations, which are traits that help organisms survive and reproduce in their environment. Adaptations can take many forms, including physical features like the beak sizes of the birds in the previous example, as well as behavioral and physiological adaptations.
One example of a behavioral adaptation is the way that some species of birds use tools to obtain food. The New Caledonian crow, for example, uses sticks to extract insects from tree bark. This behavior is not innate, but rather is learned from other crows. Over time, the ability to use tools has become an adaptation that helps these birds survive and reproduce.
Another example of a physiological adaptation is the way that some bacteria are able to resist the effects of antibiotics. Antibiotics work by killing bacteria, but some bacteria have evolved ways to counteract these effects. For example, some bacteria produce enzymes that break down the antibiotics, while others have evolved mutations that make them less susceptible to the drugs.
The Tree of Life:
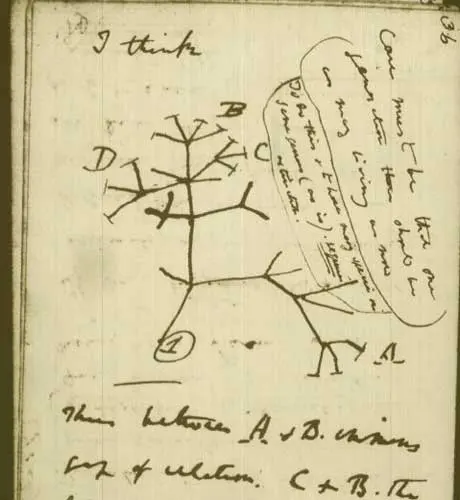
Darwin’s theory of evolution implies that all living things are related to one another through a common ancestry. This idea is represented by the “tree of life,” which is a branching diagram that shows the relationships between different species.
At the base of the tree of life is the primordial form, which gave rise to the first organisms. As the tree branches out, different groups of organisms emerge, each with their own unique adaptations and traits. For example, the vertebrates (animals with backbones) form one major branch of the tree, while the flowering plants form another.
The tree of life also shows that some groups of organisms are more closely related to one another than they are to other groups. For example, humans and chimpanzees are more closely related to one another than either is to a fish or a bird.
Common Misconceptions:
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting Darwin’s theory of evolution, there are still some common misconceptions and misunderstandings about the topic. Here are a few of the most persistent:
- Evolution is just a theory: While it’s true that evolution is a scientific theory, this does not mean that it is uncertain or unproven. In science, a theory is an explanation that has been extensively tested and supported by a large body of evidence. The theory of evolution is one of the most well-supported theories in all of science.
Read Also: Nuclear Weapon
![]()





One thought on “Darwin’s Evolution Theory”