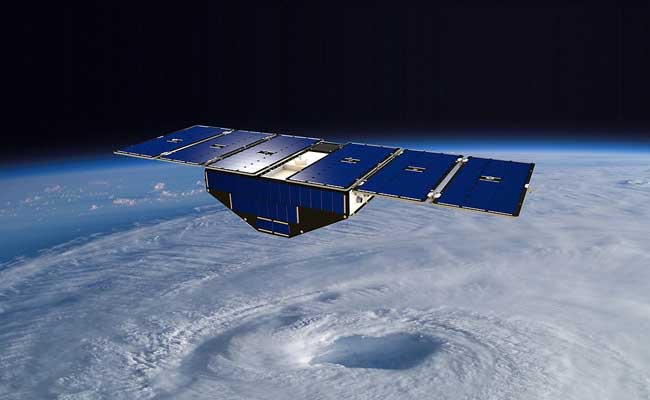
Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System: An Innovative Tool for Hurricane Forecasting
The world has seen an alarming increase in the frequency and intensity of natural disasters over the past few decades. One of the most destructive types of natural disasters is hurricanes, which can cause significant damage to both human life and property. Hurricane forecasting is a critical component of disaster management, as it allows people to prepare and evacuate in advance. With this in mind, the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) was launched by NASA in 2016 to enhance hurricane forecasting and mitigate the potential impact of these storms.
What is CYGNSS?
CYGNSS is a constellation of eight microsatellites that use GPS signals to measure the wind speed and direction of hurricanes. The satellites were designed to provide frequent and accurate measurements of hurricanes by detecting the reflected GPS signals from the ocean surface. The technology behind CYGNSS was developed by the University of Michigan and is a revolutionary approach to hurricane forecasting.
CYGNSS was launched in 2016 and is operated by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The mission is a collaboration between NASA, the University of Michigan, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). CYGNSS is part of NASA’s Earth System Science Pathfinder (ESSP) program, which aims to provide new scientific insight into the Earth’s climate and weather systems.
How does CYGNSS work?
CYGNSS uses GPS signals to measure the wind speed and direction of hurricanes. The satellites are equipped with GPS receivers that detect the reflected GPS signals from the ocean surface. The GPS signals bounce off the ocean surface, and the reflected signals are measured by the satellites. The amount of time it takes for the signals to bounce back to the satellites is used to calculate the wind speed and direction.
The CYGNSS satellites are designed to fly in a low-Earth orbit, which allows them to collect data over the same region every few hours. The satellites are placed in a constellation that provides global coverage of hurricane-prone regions. The constellation provides high-resolution measurements of the wind speed and direction of hurricanes, which can be used to improve hurricane forecasting and help predict the potential impact of these storms.
The Benefits of CYGNSS
CYGNSS provides several benefits over traditional hurricane forecasting methods. One of the main benefits is that it provides frequent and accurate measurements of hurricanes. Traditional hurricane forecasting methods rely on aircraft and buoys to collect data, which can be time-consuming and costly. CYGNSS provides continuous measurements of hurricanes, which can be used to track the storm’s progress and help predict its potential impact.
Another benefit of CYGNSS is that it provides high-resolution measurements of hurricanes. The CYGNSS satellites are designed to fly in a low-Earth orbit, which allows them to collect data over the same region every few hours. The high-resolution measurements can be used to identify the most severe parts of the storm and help predict the potential impact of these storms.
CYGNSS also provides significant cost savings compared to traditional hurricane forecasting methods. The satellites are relatively inexpensive to launch and maintain, and they provide frequent and accurate measurements of hurricanes. This can reduce the reliance on costly aircraft and buoys and provide a more cost-effective solution for hurricane forecasting.
CYGNSS Challenges
While CYGNSS provides several benefits, there are also some challenges associated with the technology. One of the main challenges is that the technology is still in its early stages of development. While the initial results are promising, more research and testing are needed to fully understand the capabilities of CYGNSS and its potential impact on hurricane forecasting.
Another challenge is that the technology requires a clear line of sight to the ocean surface to collect data.
![]()



One thought on “Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System”