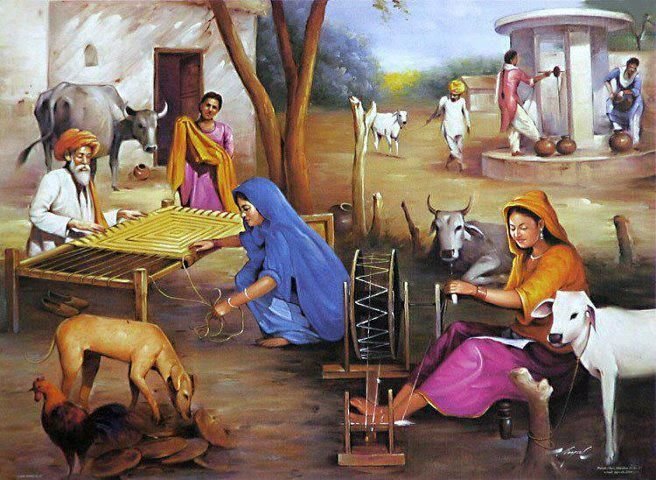
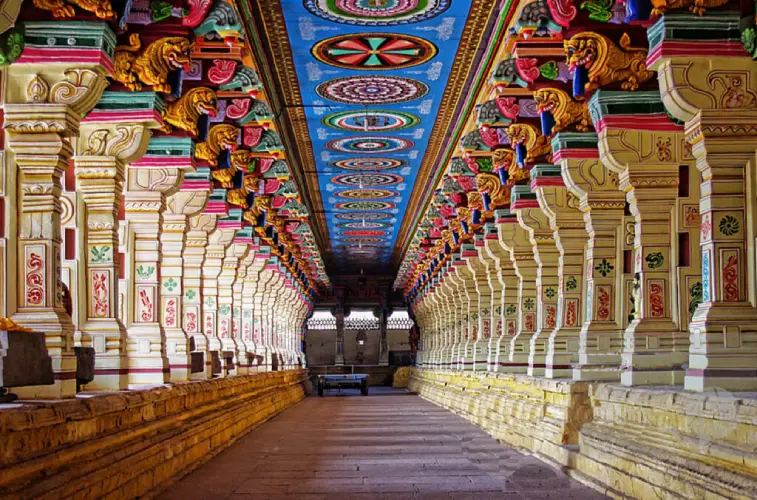
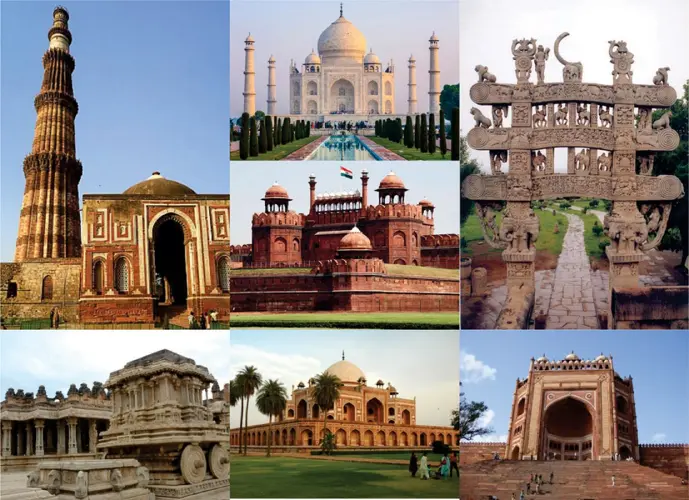
Cultural History of India: India is a land with a rich and diverse cultural history that spans thousands of years. Known for its ancient civilizations, traditions, and art forms, India’s culture is a unique blend of religious, linguistic, and social influences. From the Indus Valley Civilization to modern India, the country’s cultural evolution has shaped its identity and continues to influence societies worldwide.
Ancient Civilizations
The roots of Indian culture can be traced back to the Indus Valley Civilization (around 2500 BCE), which was known for urban planning, advanced drainage systems, and artistic achievements. This period laid the foundation for social and cultural practices, including trade, agriculture, and craftwork. The Vedic period that followed introduced Hinduism, rituals, and sacred texts like the Vedas, forming the core of India’s spiritual and philosophical traditions.
Medieval Period
During the medieval period, India witnessed the rise of various dynasties and empires, including the Mauryas, Guptas, Mughals, and Cholas. Each dynasty contributed to art, architecture, literature, and religion. The Mughal era, in particular, is known for monumental architecture like the Taj Mahal, refined music, and rich cuisine. Regional art forms, languages, and traditions flourished, creating a mosaic of cultural diversity that still exists today.
Religious and Philosophical Contributions
India’s cultural history is deeply intertwined with its religious and philosophical heritage. Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, and later Islam and Christianity influenced art, literature, festivals, and social norms. Spiritual texts, temples, and rituals not only shaped religious practices but also played a role in governance, education, and societal values. Yoga, meditation, and philosophical discourse from India have gained worldwide recognition and continue to impact global thought.
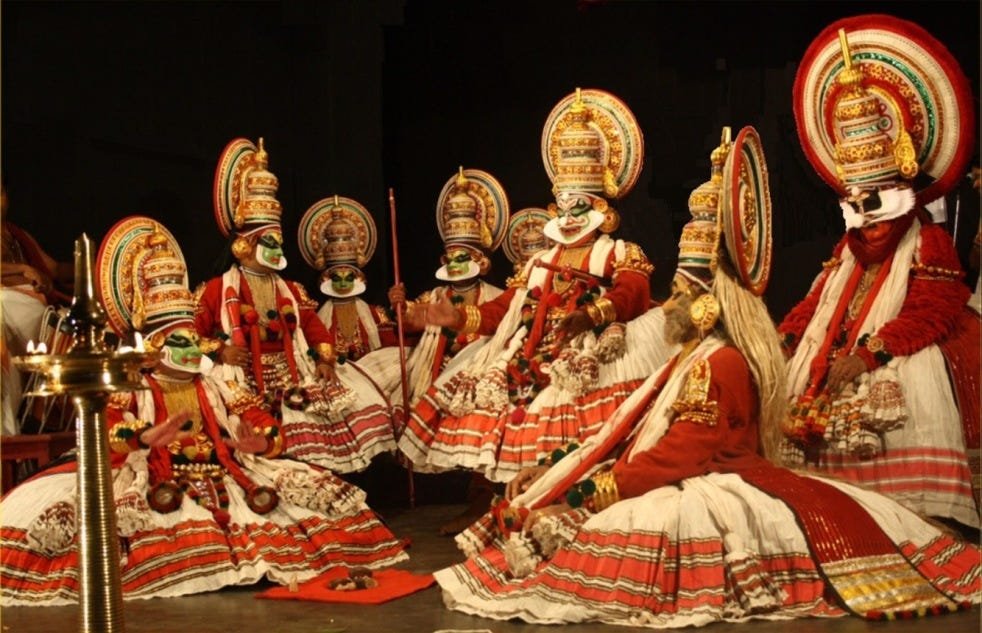

Colonial Influence and Modern India
The arrival of European powers, especially the British, introduced new cultural elements including language, education systems, and legal frameworks. Despite colonial influence, India retained its rich heritage while embracing modernization. The post-independence era saw a revival of traditional arts, music, dance, and literature, alongside advancements in science, technology, and cinema, reflecting a dynamic and evolving culture.
The cultural history of India is a testimony to its diversity, resilience, and creativity. From ancient civilizations and medieval empires to modern innovations, India’s culture continues to evolve while preserving its heritage. Understanding this history provides insight into the country’s identity, values, and contributions to the world, highlighting the enduring significance of India’s rich cultural tapestry.
Superstitious Culture in India
Lifestyle of the Indian Jarawa Tribe
![]()