Understanding Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and evidence-based approach to psychotherapy that has proven effective in treating a variety of mental health conditions. By examining the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, CBT aims to identify and modify negative patterns that contribute to psychological distress. In this article, we will explore the key principles and techniques of CBT and its applications in promoting mental well-being.
I. The Foundations of CBT: CBT is based on the notion that our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are interconnected and mutually influence one another. This approach emphasizes that it is not solely external events that determine our emotional responses but also the interpretations we attach to those events. By understanding and challenging these cognitive distortions, individuals can gain insight and develop healthier coping strategies.
II. Identifying Cognitive Distortions: CBT helps individuals recognize and reframe distorted thinking patterns that contribute to negative emotions. Common cognitive distortions include all-or-nothing thinking, overgeneralization, mental filtering, and catastrophizing. Through self-awareness and critical examination, CBT empowers individuals to challenge these distortions and replace them with more realistic and balanced thoughts.
III. Behavioral Activation: In addition to addressing cognitive distortions, CBT emphasizes the importance of modifying maladaptive behaviors. Behavioral activation encourages individuals to engage in activities that bring them pleasure or a sense of accomplishment, even when they may not feel motivated. By breaking the cycle of avoidance and withdrawal, CBT helps individuals rediscover the joy and fulfillment that can come from engaging in positive behaviors.
IV. Exposure Therapy: For individuals struggling with anxiety disorders or phobias, CBT often incorporates exposure therapy. This technique involves gradually exposing individuals to feared situations or objects in a safe and controlled manner, allowing them to confront and overcome their fears. Through repeated exposure, the anxiety response diminishes, leading to increased confidence and a reduction in avoidance behaviors.
V. Cognitive Restructuring: Cognitive restructuring is a core component of CBT, involving the identification and modification of negative thought patterns. This process helps individuals challenge irrational beliefs and replace them with more rational and adaptive thoughts. By reframing negative self-talk and self-limiting beliefs, individuals can experience improved self-esteem, reduced anxiety, and enhanced problem-solving skills.
VI. Mindfulness and Acceptance: CBT often incorporates mindfulness and acceptance-based techniques to help individuals cultivate present-moment awareness and nonjudgmental acceptance of their thoughts and emotions. Mindfulness exercises, such as meditation or deep breathing, promote relaxation and emotional regulation, enabling individuals to respond more effectively to stressful situations.
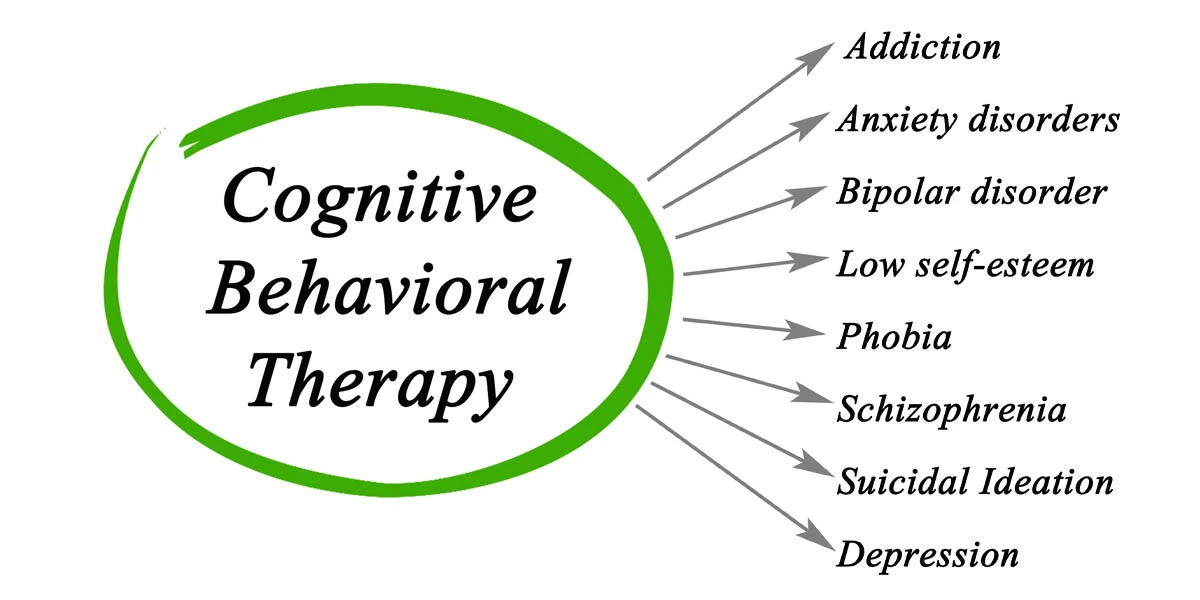
VII. Applications of CBT: CBT has been extensively researched and found to be effective in treating various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and eating disorders. It is also utilized in the management of chronic pain, insomnia, and substance use disorders. CBT can be delivered in individual or group settings and is often combined with other therapeutic approaches for optimal outcomes.
Conclusion: Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a structured and practical approach to addressing cognitive distortions and maladaptive behaviors that contribute to mental health challenges. By helping individuals recognize and challenge negative thoughts, modify behaviors, and develop healthy coping strategies, CBT empowers individuals to take control of their mental well-being. As a versatile and evidence-based therapy, CBT continues to be a valuable tool in promoting lasting positive change and improving overall quality of life.
![]()