Boreal Forest: The boreal forest, also known as taiga, is a unique category of forest that spans across the Northern Hemisphere. Covering vast areas of land, the forest is an important ecosystem that supports a diverse range of plant and animal species. In this article, we will explore the forest, its characteristics, and why it is an important ecosystem.
Geographical Location:
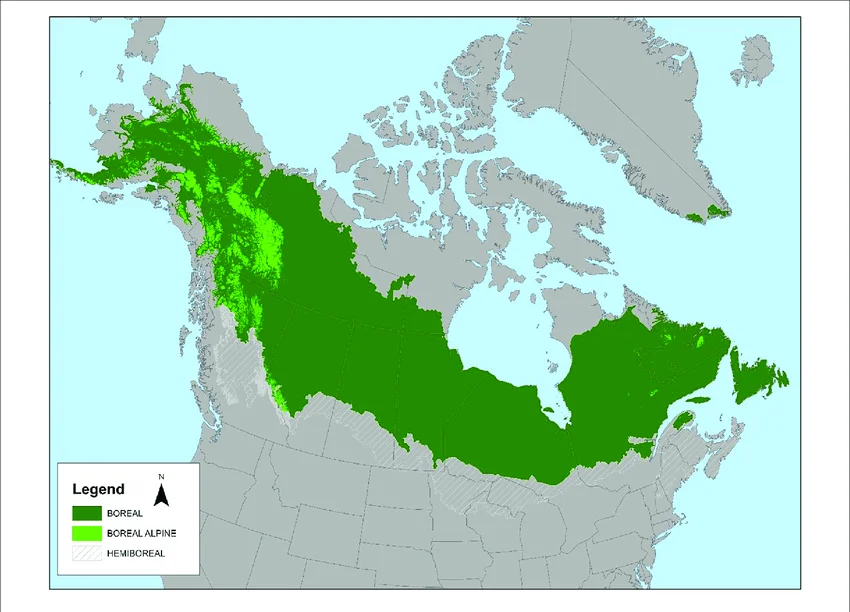
The boreal forest covers a significant portion of the Northern Hemisphere, stretching from Alaska in North America to Scandinavia in Europe and from Russia in Asia to the northern edges of China and Japan. It is the largest terrestrial ecosystem on the planet and spans over 11 million square kilometers.
Climate:
The boreal forest experiences long, cold winters and short, cool summers. The average temperature during the winter can reach as low as -40°C, while the summer temperatures can range from 10°C to 20°C. The extreme temperatures and short growing season limit the diversity of plant and animal species that can survive in the forest.
Flora:
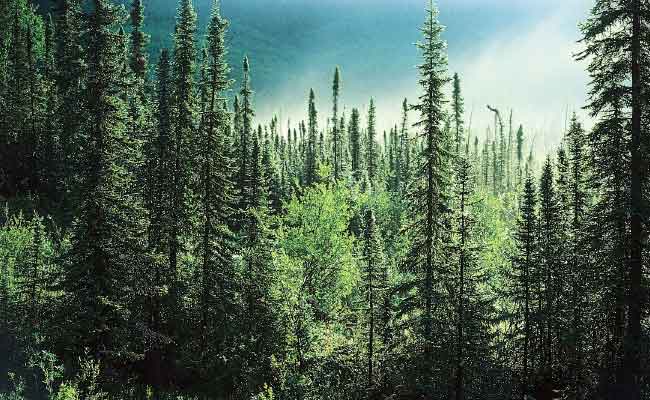
The forest is dominated by coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, and fir, which are well-adapted to the cold and dry climate. These trees have needles instead of leaves, which helps them conserve water during the long, dry winters. Other common plant species in the forest include deciduous trees, such as aspen and birch, as well as shrubs, mosses, and lichens.
Fauna:
The boreal forest supports a diverse range of animal species, including mammals, birds, fish, and insects. Some of the most iconic animal species in the forest include moose, caribou, lynx, wolves, bears, and beavers. The forest is also an important habitat for migratory birds, such as waterfowl, songbirds, and raptors. Many of these animals have adapted to the harsh climate and rely on the forest for their survival.
Importance of the Boreal Forest:
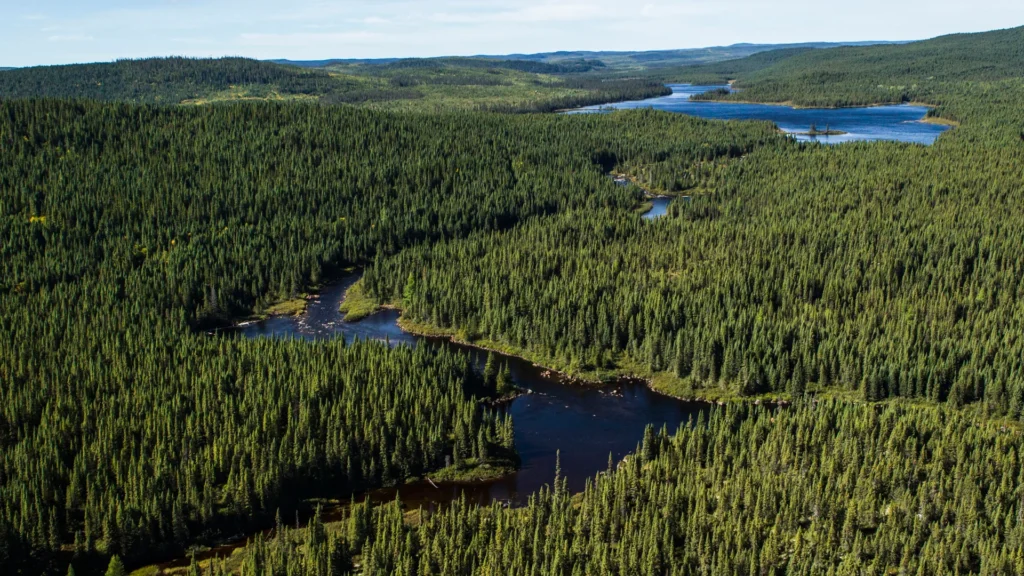

The boreal forest is an important ecosystem that provides a wide range of ecological, economic, and cultural benefits. Here are some of the key reasons why the forest is important:
- Carbon Storage: The boreal forest plays a critical role in the global carbon cycle by storing vast amounts of carbon in its trees and soil. In fact, the forest stores more carbon than any other terrestrial ecosystem on the planet. This makes it an important tool in mitigating climate change.
- Biodiversity: The boreal forest supports a diverse range of plant and animal species, many of which are adapted to the cold and dry climate. It is also an important breeding ground and migration route for many bird species.
- Timber: The boreal forest is an important source of timber, which is used for a wide range of products, including paper, furniture, and building materials. However, it is important to manage the forest sustainably to ensure that it can continue to provide these benefits in the long term.
- Cultural Heritage: The boreal forest has been an important part of the cultural heritage of Indigenous Peoples for thousands of years. It provides important resources for food, medicine, and traditional practices.
Threats to the Boreal Forest:
Despite its importance, the forest is facing a range of threats, including:
- Climate Change: The forest is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, including increased temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and more frequent and severe wildfires.
- Industrial Development: The forest is under increasing pressure from industrial development, including logging, mining, and oil and gas extraction. These activities can have negative impacts on the forest ecosystem and the species that depend on it.
Read Also: Yosemite National Park
![]()






2 thoughts on “Boreal Forest”