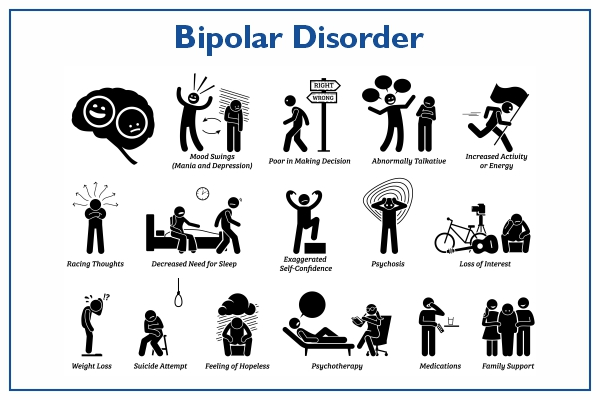
Bipolar disorder, also known as manic-depressive illness, is a highly complex mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. With severe mood swings, episodes of intense mania, and deep depression, manic-depressive illness can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life and relationships. In this article, we will discuss the key aspects of manic-depressive illness, its types, symptoms, causes, treatment options, and coping strategies in more depth.
Types of Bipolar Disorder:
Bipolar disorder can manifest in different forms, with bipolar I and bipolar II being the most common types. Bipolar I involves manic episodes that can last for a week or more, often accompanied by depressive episodes. On the other hand, bipolar II involves hypomanic episodes that are less severe than full-blown mania, along with depressive episodes. Recognizing the differences between these two types is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Signs and Warning Signs of Bipolar Disorder:
The symptoms of this Disorder can vary widely, making it difficult to diagnose. Manic episodes are characterized by excessive energy, increased euphoria, impulsivity, and a decreased need for sleep. On the other hand, depressive episodes include feelings of sadness, hopelessness, loss of interest, changes in appetite, and sleep disturbances. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms early and seek professional help for effective intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors:
While the exact causes of bipolar disorder are not yet fully understood, genetic, biological, and environmental factors are believed to play a role in its development. People with a family history of bipolar are at higher risk, as are people with neurotransmitter imbalances and hormonal irregularities in the brain. Identifying these risk factors can help with the early detection and management of the condition.

Impact on Daily Life:
Living with bipolar can have a profound impact on a person’s daily life and relationships. Unpredictable mood swings can make it challenging to maintain stable employment, educational pursuits, and interpersonal connections. Establishing a support network and adopting coping strategies are essential to managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Treatment options:
Fortunately, bipolar disorder is a treatable condition, and with the right approach, individuals can live fulfilling lives. Treatment usually involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Mood stabilizers, antidepressants, and antipsychotic medications are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms, while psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals develop coping skills and identify triggers.
Self-care and coping strategies:
In addition to professional treatment, self-care plays an important role in managing bipolar disorder. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress reduction strategies can help relieve symptoms. Establishing a routine, maintaining a support system, and avoiding substance abuse are also essential to effectively managing this condition.
Breaking the stigma:
People with manic-depressive illness often face stigma and misconceptions about the mental health condition. Raising awareness, promoting open dialogue, and challenging stereotypes can help break down these barriers. Providing a safe and inclusive environment for people with bipolar disorder to support their well-being and recovery is essential.
Finally, understanding bipolar disorder and its complications is essential for effective diagnosis, treatment, and management. By identifying the symptoms, causes, and available treatment options, people with manic-depressive illness can live fulfilling lives and effectively manage their symptoms. With early intervention, a comprehensive treatment plan, and ongoing support, people with bipolar disorder can overcome the challenges of this mental health condition and thrive. Let’s continue to break down the stigma surrounding mental health and support people with bipolar on their journey to recovery and well-being.
Read Also: Diu Beach Getaways: A Tranquil Coastal Escape
![]()