Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Complex Neurodevelopmental Condition
Introduction:
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent challenges in social interaction, communication, and restrictive and repetitive patterns of behavior. It affects individuals across the lifespan and can significantly impact their daily functioning and quality of life. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of ASD, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available interventions.
- What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
ASD is a complex and heterogeneous disorder that encompasses a range of conditions previously diagnosed separately, such as autistic disorder, Asperger’s syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS). It is now classified under a single umbrella term, Autism Spectrum Disorder.
- Symptoms and Challenges:
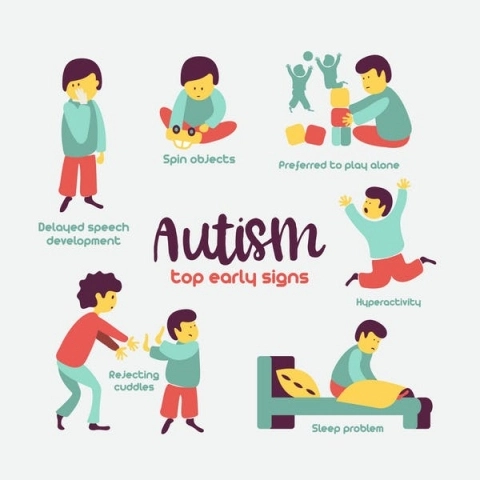
Individuals with ASD often face challenges in social communication and interaction. They may struggle with understanding and using nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language. Difficulties in maintaining eye contact and engaging in reciprocal conversations are common. Restricted interests, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities are also frequently observed.
- Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact causes of ASD are not yet fully understood, but research suggests a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as certain gene mutations and chromosomal abnormalities have been associated with the disorder. Environmental influences, such as prenatal exposure to certain substances, complications during birth, and advanced parental age, may also contribute to the development of ASD.
- Diagnosis and Screening:
Diagnosing ASD involves comprehensive assessments by medical professionals, including psychologists, psychiatrists, and developmental pediatricians. Observations of behavior, interviews with caregivers, and standardized tests are conducted to evaluate social communication skills, language abilities, and behavioral patterns. Early screening and intervention are crucial for timely support and better outcomes.
- Treatment and Interventions:
While there is no known cure for ASD, various interventions and therapies can help individuals with the disorder manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is one of the most widely used interventions, focusing on promoting desired behaviors and reducing challenging ones. Speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training are also beneficial in addressing specific needs.
- Support for Individuals with ASD:
Supportive environments and understanding communities play a crucial role in facilitating the well-being of individuals with ASD. Schools and educational institutions can implement inclusive practices to accommodate their unique needs. Parent support groups and counseling services offer valuable assistance to families, providing them with resources and strategies to cope with the challenges associated with ASD.
- Advances in Research and Awareness:
Research into ASD continues to expand our understanding of the disorder. Advancements in neuroscience, genetics, and behavioral sciences contribute to the development of more targeted interventions and personalized treatments. Increased awareness and acceptance of autism in society foster a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with ASD.
Conclusion:
Autism Spectrum Disorder is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals in various ways. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available interventions is essential for early diagnosis, support, and improved outcomes. By promoting acceptance, awareness, and inclusive practices, we can create a society that embraces the strengths and diversity of individuals with ASD, empowering them to reach their full potential.
![]()