The Antibody Conjugate is Effective Against Brain Metastases: Brain metastases, where cancer spreads to the brain from other parts of the body, pose significant challenges in oncology. Conventional treatments often fall short because of the blood-brain barrier, making it difficult for standard chemotherapy and radiation to effectively target these lesions. However, recent advances in cancer treatment have introduced antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) as a promising solution for the management of brain metastases. This article explores the efficacy of antibody conjugates and their potential to revolutionize treatment options for patients with brain metastases.
Understanding antibody-drug conjugates:
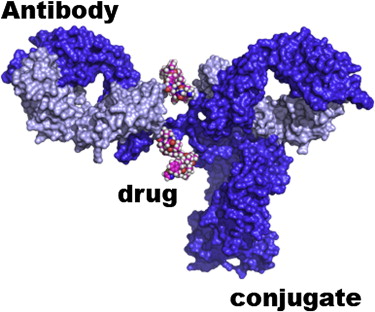
Antibody-drug conjugates are innovative therapies that combine monoclonal antibodies with cytotoxic drugs. Antibodies are designed to specifically target cancer cells, delivering powerful drugs directly to the tumor and minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. This targeted approach improves therapeutic efficacy while reducing side effects, a common problem with conventional chemotherapy.
The mechanism behind ADCs involves the binding of antibodies to specific antigens expressed on cancer cells. Once bound, the ADC is internalized by the cell, releasing the cytotoxic drug and leading to cell death. This precision targeting is particularly important in the treatment of brain metastases, where preservation of healthy brain tissue is critical.
Why ADCs are effective against brain metastases:
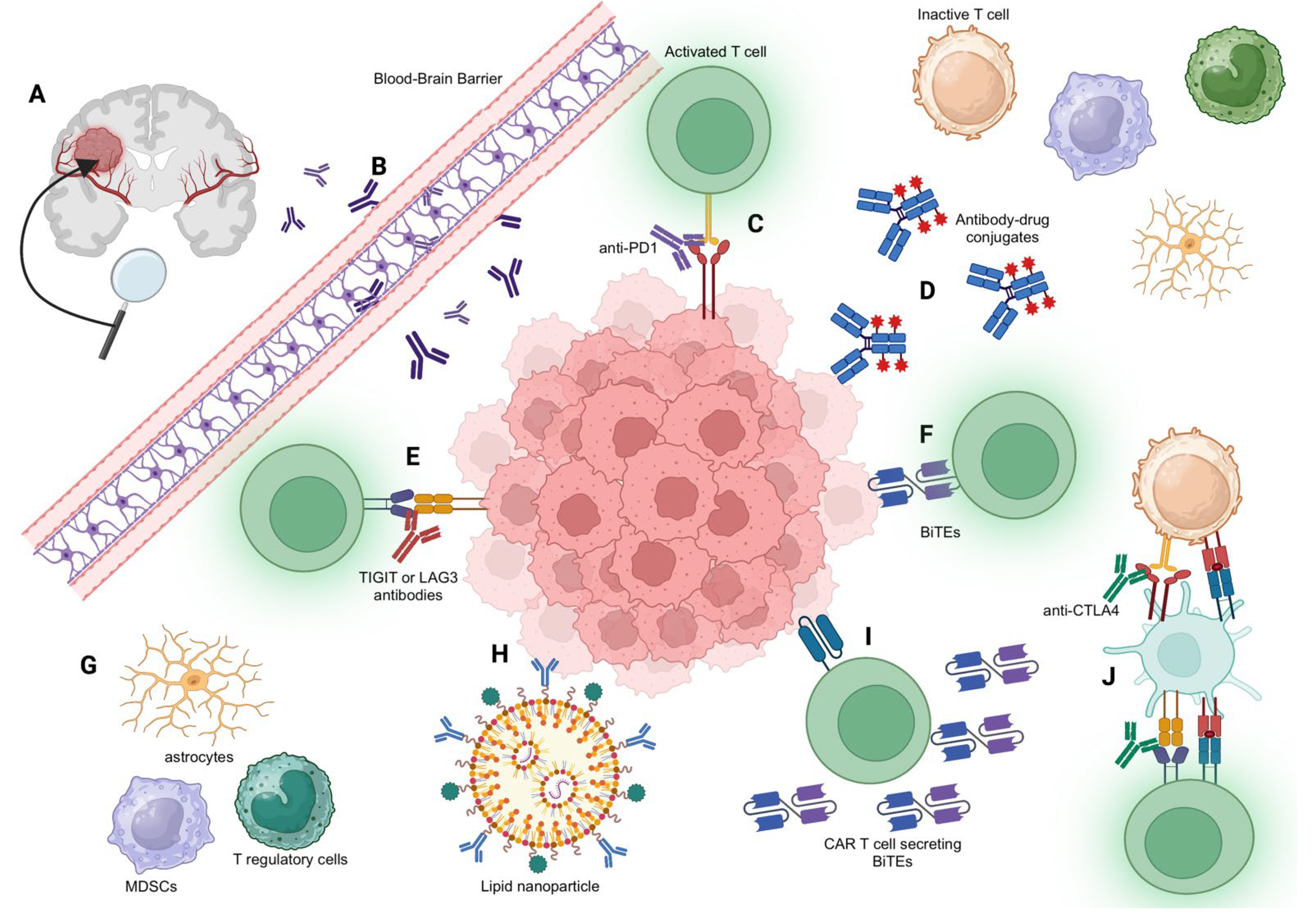
Targeted delivery: One of the primary advantages of ADCs is their ability to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells. In the context of brain metastases, this targeted delivery is essential to overcome the limitations of the blood-brain barrier, which often prevents effective systemic treatment.
Reduced systemic toxicity: By focusing treatment on cancer cells, ADCs can significantly reduce the side effects typically associated with chemotherapy. Patients undergoing ADC treatment may experience fewer adverse reactions, improving their overall quality of life.
Improved response rate: Clinical studies have shown that ADC can lead to higher response rates in patients with brain metastases. This is particularly notable in cancers such as breast cancer and lung cancer, where ADCs have demonstrated considerable efficacy in reducing tumor size and improving survival rates.
Combination potential: ADCs can be combined with other treatment modalities, such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy. This combination approach allows for a more comprehensive treatment strategy, potentially leading to better outcomes for patients with complex metastatic disease.
Current research and development The Antibody Conjugate is Effective Against Brain Metastases:
Ongoing research into ADC is yielding promising results. For example, novel ADCs targeting specific antigens associated with brain metastases are in various stages of clinical trials. The goal of these trials is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new agents, providing hope for better treatment options for patients who previously had limited options.
Additionally, advances in technology are enabling the development of more potent and selective ADCs. Innovations in linker chemistry and drug design are increasing the stability and efficacy of these conjugates, making them more suitable for targeting brain metastases.
Challenges and Considerations for the Antibody Conjugate is Effective Against Brain Metastases:

Despite the promise shown by ADCs, several challenges remain. A significant concern is the potential for resistance to therapy, as cancer cells can develop mechanisms to evade the effects of targeted treatments. Continued research is needed to understand these resistance mechanisms and develop strategies to overcome them.
Furthermore, central nervous system complications require careful consideration of dosage and administration. Clinical trials must confirm that ADCs can effectively penetrate the blood-brain barrier without compromising patient safety.
Antibody-drug conjugates represent a transformative approach in the fight against brain metastases. With their targeted delivery, reduced toxicity, and improved response rates, ADCs offer new hope for patients facing this dire diagnosis. Ongoing research and development will be critical to maximizing the potential of this innovative therapy, paving the way for more effective treatment strategies. As understanding of ADCs continues to evolve, we are moving closer to providing patients with the targeted care they need to effectively deal with brain metastases.
In summary, the efficacy of antibody conjugates against brain metastases highlights the potential of precision medicine in oncology, making it a key area for future exploration and investment in cancer treatment.
Read Also: A Novel Approach to Overcoming Barriers for All Patients
![]()



One thought on “The Antibody Conjugate is Effective Against Brain Metastases”