Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC) is a potent technology that facilitates real-time data, audio, and video sharing between web browsers and mobile apps. It eliminates the need for plugins or external software and allows seamless peer-to-peer communication. In this article, we’ll explore how WebRTC works, its core components, and why it is essential for modern web applications.
What Is WebRTC?
WebRTC is an open-source project supported by major browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge. It provides developers with APIs that enable real-time communication capabilities such as video calls, voice calls, live streaming, and file sharing directly within a browser.
WebRTC is widely used in applications like video conferencing platforms, online customer support, telemedicine, gaming, and collaboration tools.
Core Components of WebRTC
WebRTC works through three main APIs that handle different aspects of communication:
1. MediaStream API
The MediaStream API is responsible for capturing audio and video from the user’s device, such as a microphone or webcam. It allows browsers to request permission from users before accessing their media devices. Once permission is granted, the media stream can be transmitted in real time to another peer.
2. RTCPeerConnection API
RTCPeerConnection is the backbone of WebRTC communication. It manages the connection between two peers and handles the transmission of audio, video, and data efficiently. This API takes care of codec selection, bandwidth optimization, network adaptation, and encryption to ensure secure and smooth communication.
3. RTCDataChannel API
RTCDataChannel allows browsers to exchange arbitrary data directly, such as text messages, files, or game data. This feature enables real-time data transfer with low latency, making WebRTC suitable for chat applications, multiplayer games, and collaborative tools.
How WebRTC Establishes a Connection
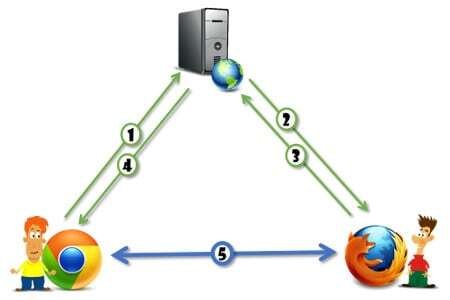
WebRTC uses a step-by-step process to establish a peer-to-peer connection:
Signaling Process
Before communication starts, peers must exchange information about their capabilities. This process is known as signaling. WebRTC does not define a signaling method, so developers can use WebSockets, HTTP, or other protocols to exchange Session Description Protocol (SDP) data.
ICE, STUN, and TURN Servers
To connect peers across different networks, WebRTC uses ICE (Interactive Connectivity Establishment). ICE works with STUN and TURN servers to determine the best possible path between peers.
- STUN servers help discover public IP addresses.
- TURN servers relay data when direct peer-to-peer communication is not possible.
This ensures WebRTC works even behind firewalls or NATs.
Secure Peer-to-Peer Connection
Once signaling and ICE negotiation are complete, WebRTC establishes a secure peer-to-peer connection. All media and data transmitted through WebRTC are encrypted using DTLS and SRTP, ensuring privacy and security.
Why WebRTC Is Fast and Efficient
WebRTC is designed for low latency and high performance. It dynamically adjusts video quality based on network conditions and uses advanced codecs like VP8, VP9, H.264, and Opus. These optimizations ensure smooth communication even on slow or unstable networks.
Common Use Cases of WebRTC
WebRTC is widely adopted across industries, including:
- Video conferencing and online meetings
- Live customer support and chat systems
- Telehealth and remote consultations
- Online education and virtual classrooms
- Real-time collaboration tools
Its flexibility and browser support make it a preferred choice for developers.
Benefits of Using WebRTC
Some key advantages of WebRTC include:
- No plugins or downloads required
- Cross-platform and cross-browser compatibility
- Secure, encrypted communication
- Low latency and high-quality streaming
- Open-source and developer-friendly
WebRTC works by enabling secure, real-time peer-to-peer communication using powerful browser APIs and networking protocols. From capturing media to establishing encrypted connections, WebRTC simplifies real-time communication for modern web applications. As demand for instant and interactive experiences continues to grow, WebRTC remains a critical technology shaping the future of online communication.
What Happens After the Death of a Human
Survival of the Fittest Theory by Charles Darwin
Read Also: Education Website Design
![]()